Renewable generation continues record-breaking streak, putting pressure on power prices – report
Renewable energy set a new record level in August with 25.6% of electricity supplied across the NEM, according to a new report by a progressive think-tank, The Australia Institute. This volume of new generation is likely to significantly increase competition in the wholesale market, thereby putting downward pressure on prices, the report finds.
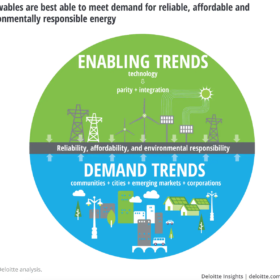
Deloitte: The case for renewables has never been stronger
Renewable energy sources, notably solar and wind, are reaching price and performance parity on and off the grid, shows a new Deloitte Global report, highlighting seven trends that are driving this transformation.
Victorians invited to apply for rooftop solar rebates
Applications have officially opened for 50% rebates on rooftop solar installations under the Victorian government’s Solar Homes program, announced just weeks ago. The subsidies will be available until 30 June next year.
AEMO gets green light to set up distributed solar+storage register
Australia’s policy maker for the energy markets has approved the establishment a national register of small-scale distributed energy resources, which will give AEMO and distribution network businesses more data to help in planning and operating the power system as it transforms.
Victorian auction winners outline construction plans
The developers that emerged as winners in the Victorian government’s first renewable energy auction have confirmed receiving support agreements from the state to ensure revenue certainty for the projects. The companies have also outlined their construction plans, some of which even include batteries.
Mining sector to rely increasingly on renewables, report finds
As mining companies become more aware of the rapidly falling costs of renewables, wind and solar are set become a growing trend in powering mining operations worldwide over the coming years, shows a new report from Fitch Solutions. On the back of carbon pricing schemes, countries and companies operating in the Americas are best positioned to lead the way in the adoption of renewables in mining.
California governor signs 100% clean electricity bill
SB 100 puts California on a path to 100% zero-carbon electricity. What does that mean for the rest of the nation?
Victoria announces first RE auction winners, pledges battery subsidy scheme
Although initially expected to deliver around 650 MW, Victoria’s first renewable energy auction has smashed the goal, delivering 928 MW of renewable capacity. Six projects will be developed in total, three wind and three solar, under the state’s renewable energy target. In a separate announcement, the Andrews government promised to provide half price solar batteries for 10,000 Victorian households, if re-elected.
Report: 100% RE electricity by 2030 possible
By keeping up the current rate of solar PV and wind deployment, Australia is forecast to comfortably exceed the 2020 RET of 33,000 GWh, achieve 26% emissions reduction by 2020/21 and meet its Paris greenhouse emissions target in 2024/25, shows new analysis by the Australian National University (ANU). In 2018 and 2019 combined, over 10 GW of renewable energy could be installed.
SA unveils details of $100 million battery scheme, sonnen sets up production plant in Adelaide
The South Australian government will launch its Home Battery Scheme in October, which will offer South Australians subsidies of up to $6,000. In the wake of the government’s announcement, the German storage provider has revealed plans to manufacture up to 50,000 battery storage units at the former Holden site in Elizabeth, creating hundreds of jobs.