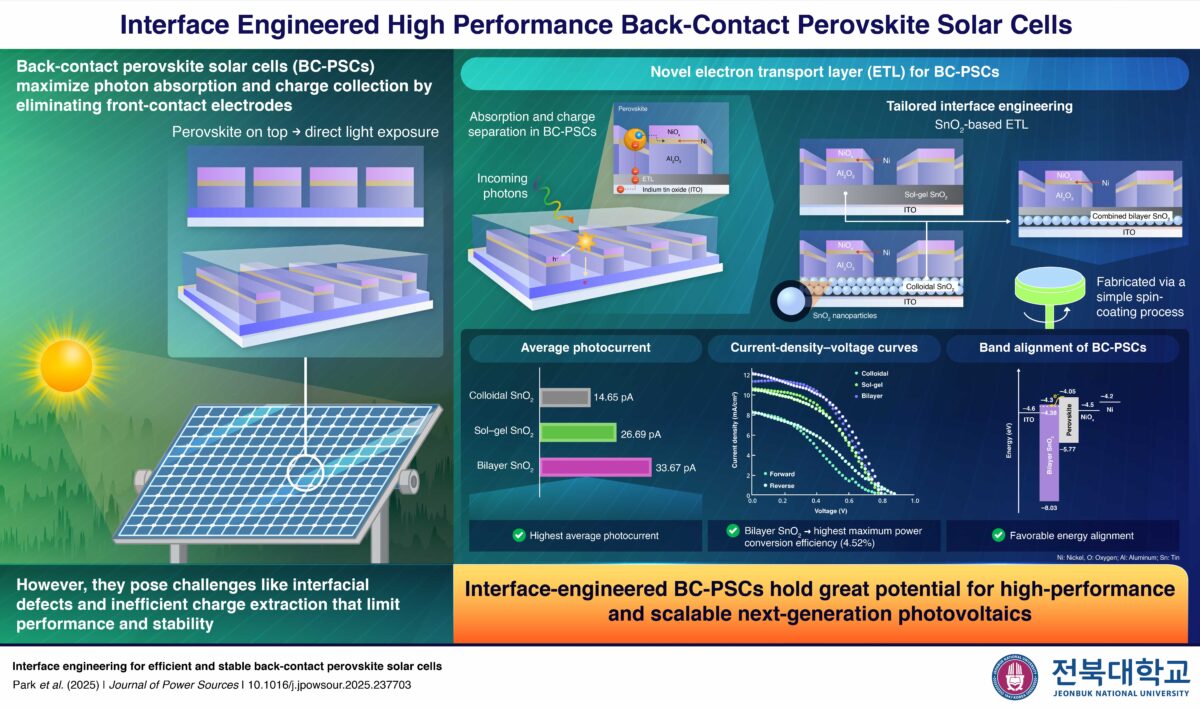
Researchers from the University of Seoul (UOS) and Joenbuk National University (JNU) in South Korea have developed a novel bilayer tin oxide (SnO2) electron transport layer (ETL), via a simple spin-coating method, that significantly improves efficiency and stability of back-contact perovskite solar cells (BC-PSCs).
The Interface engineering for efficient and stable back-contact perovskite solar cells study, led by UOS Department of Chemical Engineering Associate Professor Min Kim and JNU School of Chemical Engineering PhD student Dohun Baek, was published in the Journal of Power Sources.
“We selected SnO2 for the ETL due to its favorable conduction band alignment with perovskite and superior electron mobility compared to conventional titanium oxide,” Kim explained.
“As a result, our bilayer ETL enhances interfacial contact, reduces recombination losses, and optimises energy alignment for electron charge carriers.”
To evaluate the role of ETL engineering, the researchers fabricated three BC-PSC devices with different SnO2-based ETLs: a colloidal SnO2 made of nanoparticles, a sol-gel SnO2, and a bilayer SnO2 consisting of a nanoparticle SnO2 layer combined with a sol-gel layer. Each ETL was spin-coated onto indium tin oxide substrates and patterned via photolithography.
A series of experiments compared the performance of the devices, which showed that the device with bilayer SnO2 yielded the highest average photocurrent of 33.67 picoampere (pA), outperforming the sol-gel SnO2 device at 26.69 pA and colloidal SnO2 device at 14.65 pA.
The bilayer SnO2 device also achieved a maximum power conversion efficiency of 4.52%, was the highest of the three, and improved operational stability, owing to its enhanced suppression of charge recombination.
“BC-PSC devices hold great promise for a variety of applications, including flexible devices and large-area solar modules, due to their high efficiency, enhanced stability, and scalable design” Baek said.
“We believe our findings will help accelerate the development of practical BC-PSC technologies for real-world applications while advancing sustainable energy solutions.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.






By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.