From pv magazine USA
London-headquatered Highview Power has contracted with Nebraska-based Tenaska Power Services to help develop up to four gigawatt-hour scale cryogenic energy storage plants in the United States over two years, with the first project expected to be developed in the ERCOT market.
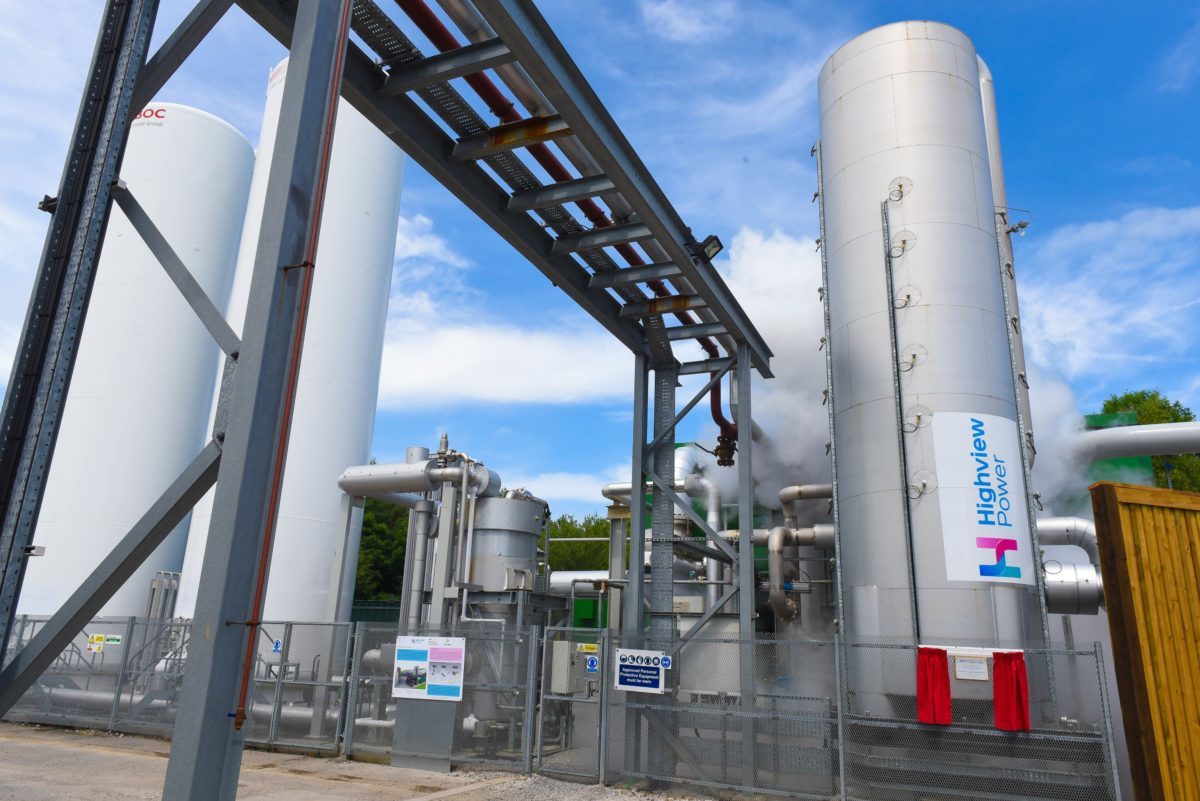
Highview’s technology uses electricity to chill and liquefy air at -320°F, stores the liquid air in insulated, low-pressure tanks, and later exposes the liquid air to ambient temperatures to rapidly re-gasify the air, expanding it to 700 times its liquid volume, to power turbines to generate electricity. The firm notes that its system can be configured to also use waste heat and cold.

Highview has been operating a 5-megawatt cryogenic energy storage facility in Manchester, England since June 2018.
Highview Power says the levelized cost is $140/MWh for a 200 MW/2 GWh (10-hour) system, with no use of waste heat or cold. The firm adds that its technology permits “weeks’ worth of storage,” with the use of additional tanks.
For comparison, Lazard has estimated that battery storage has a levelized cost of $108 to $140 per MWh for a utility-scale PV-plus-storage application. All cost estimates are sensitive to the assumptions used, particularly the capital cost, and the cost of capital.
Highview sees ERCOT as a promising market because it is “a big wind market—we can co-locate with wind resources to store power during off-peak hours,” said Javier Cavada, president and CEO of Highview Power, in a pv magazine interview.
The cryogenic energy storage technology can support “intermittent renewable generation, energy arbitrage, peak shaving, ancillary services, transmission and distribution deferral, inertia services, reactive power, and voltage support,” he said.
Highview’s pilot-scale facility in England uses waste heat from adjacent landfill gas engines, said Cavada, and the technology can also use waste cold—for example, from an LNG import terminal, where liquified natural gas is being re-gasified to put on a gas distribution network. He said that LNG process may use sea water to warm the LNG, thus chilling the sea water, and “the cold is simply being dumped.”
Highview expects to begin construction of the first U.S. plants within two years, Cavada added.
The specific role of Tenaska Power Services will be to “identify, model, optimize and provide energy management services” for cryogenic energy storage projects.
Tenaska Power Services, a business unit of Tenaska, is a power marketing firm that “offers utilities, municipalities, large industrial clients and independent power producers a variety of optimization, risk management, power trading and settlement services.”
Highview Power previously entered a joint venture with TSK, an EPC firm headquartered in Spain, to co-develop cryogenic storage projects in Spain, the Middle East, and South Africa. Highview has also partnered with the Finland-based global engineering firm Citec to modularize its gigawatt-hour scale technology.
Author: William Driscoll
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.







By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.