From pv magazine France.
Eight months ago, a state-funded French research institute and Japanese textiles company Toyobo announced they would join forces to develop superior organic solar cells for indoor applications. The partnership, the French organization said at the time, was aimed at developing thin, flexible solar cells which could function where conventional, inorganic solar cells could not.
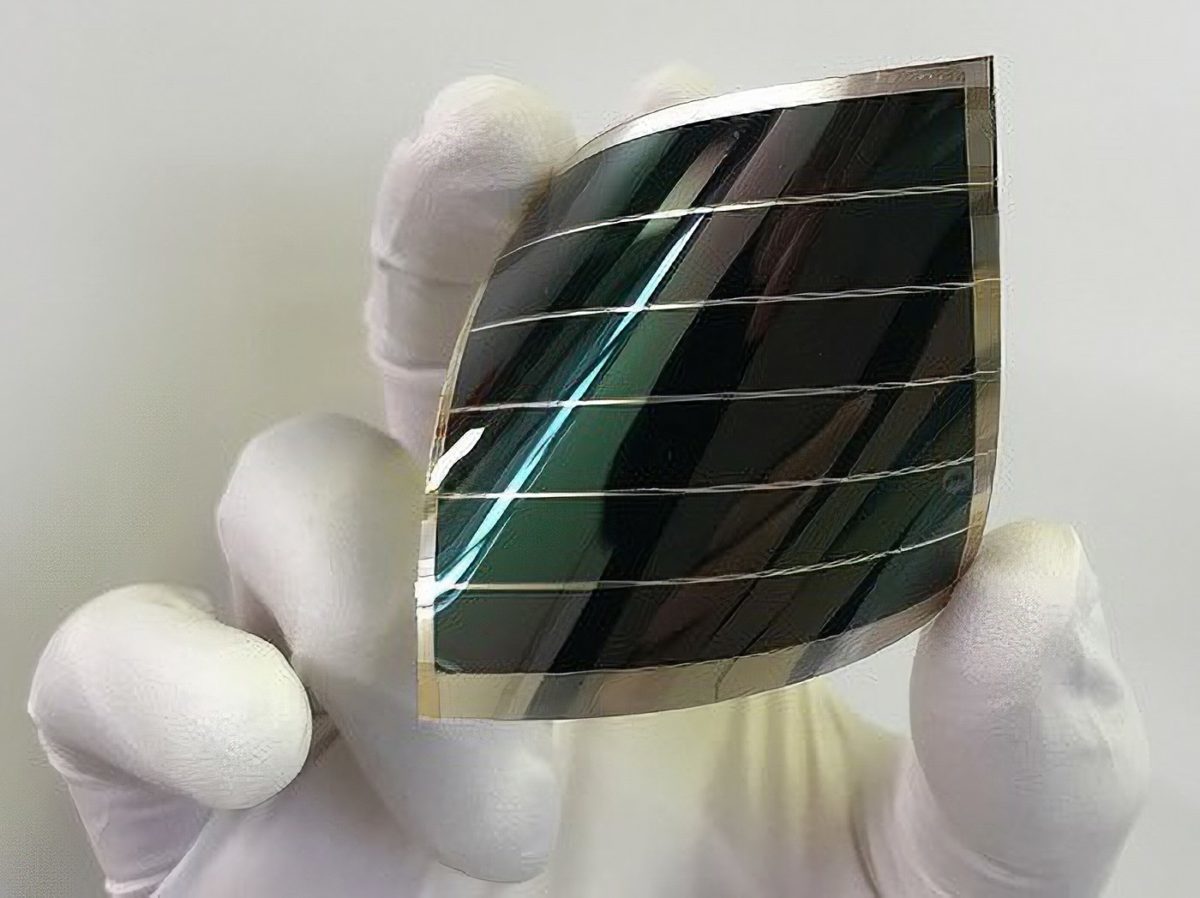
The new energy technologies and nanomaterials (Liten) division of the French Alternative Energies and Atomic Energy Commission and Toyoba have published the first results of six months of research: small organic solar cells they say offer the “best conversion efficiency in the world in a dark room”.
“During a verification experiment under neon lighting of 220 lux – equivalent to the brightness of a dark room – it was confirmed that the product tested had achieved a conversion efficiency of about 25%, or 60% more than that of amorphous silicon solar cells commonly used for pocket calculators,” said Liten and Toyobo. The latter firmed up the claim by stating it measured efficiency of 16% under the same brightness for amorphous silicon devices.
PET project
The researchers used an energy-generating material developed by Toyobo which uses organic synthesis technology the company created during years of research in fine chemistry. “This material can dissolve easily, even in halogen-free solvents, allowing it to be applied uniformly on a substrate and to produce energy stably with few individual differences,” said the Japanese company. The research group optimized the solvents and the technique of coating the organic cells on a glass substrate.
Liten and Toyobo have also developed prototypes of organic solar modules on a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film substrate over an effective area of 18cm2, despite the increased difficulty of applying on PET film. That module was able to produce around 130 microwatts (µW) under 220 lux lighting, according to its developers.
Toyobo stated its new materials would be offered to solar cell manufacturers with the aim of hitting commercial production within three years, primarily as a wireless power source for temperature-humidity and motion sensors.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.







By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.