Researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) School of Electrical Engineering have developed electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technology that can improve the stability and performance of high-capacity batteries in electric vehicles (EV).
The technology can precisely diagnose and monitor the state of EV batteries using small amounts of currents to measure the resistance to current flow within the battery and assess battery performance and condition.
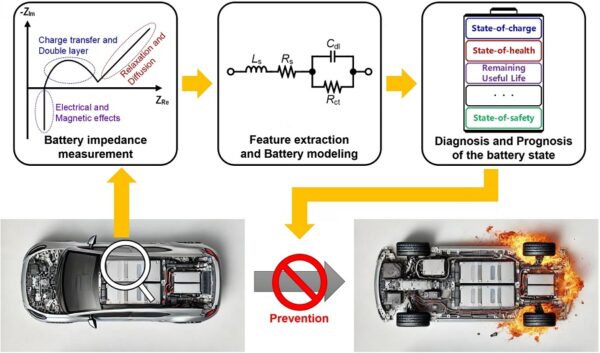
Image: Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology
Traditional EIS equipment is difficult to install, operate, and maintain due to cost and complexity, and can cause significant electrical stress, increasing the risk of battery failure or fire and making it difficult to use in practice.
KAIST’s EIS system can precisely measure battery impedance with low current disturbances (10mA), minimising thermal effects and safety issues during the measurement process.
In addition, the system minimises bulky and costly components, making it easy to integrate into vehicles.
The system was proven effective in identifying the electrochemical properties of batteries under various operating conditions, including different temperatures and SOC levels.
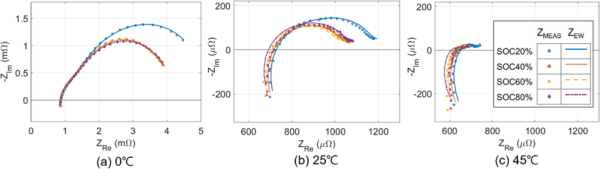
Image: Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology
KAIST Professor Kyeongha Kwon said the system can be easily integrated into the battery management system (BMS) of electric vehicles and has demonstrated high measurement accuracy.
“It can contribute to battery diagnosis and performance improvements not only for electric vehicles but also for energy storage systems (ESS),” Kwon said.
Findings have been published in the United States-headquarted Institute of Electrical Engineers (IEEE) Transactions on Industrial Electronics journal, titled Small-Perturbation Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy System With High Accuracy for High-Capacity Batteries in Electric Vehicles.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.








1 comment
By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.