Data from the Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) shows the “wave” of renewable energy projects moving through the connections pipeline for the National Electricity Market (NEM) continued to grow in 2024 with 49.6 GW of capacity in progress at the end of the year, up from 36.4 GW at the end of 2023.
Margarida Pimentel, manager of AEMO’s onboarding and connections group, said the market operator’s latest Connections Scorecard for the NEM highlights the surge of solar, wind and battery projects navigating the grid connection process.
“Given the NEM’s total generation and storage capacity of 66 GW, nearly 50 GW of new projects marks a significant pipeline of future energy supply,” she said.
The scorecard shows about 36% of this capacity was in New South Wales (NSW), 32% in Queensland, 21% in Victoria and 10% in South Australia.
“The scorecard data also reveals that 18.1 GW out of the 49.6 GW within the connections pipeline are battery projects, representing a 97% increase on the 9.2 GW in progress during the same time last year,” Pimentel said.
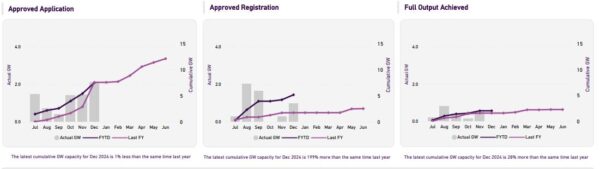
Image: AEMO
AEMO’s latest data also highlights the increasing momentum in project registrations, with 1.7 GW registered in the December quarter and 5.2 GW over the past six months.
“Project registrations in the last six months are more than double those in the previous 12 months,” Pimentel said. “This surge reflects the wave of application approvals in 2023.”
Eleven projects were registered during the December quarter with solar accounting for 831 MW, followed by wind (440 MW), and batteries (350 MW), with 52% of the capacity registered in NSW.
“These registered projects are built, connected to the grid and can now move through to the final commissioning phase,” Pimentel said.
The momentum of new connection applications also continued to build in the December quarter, with 16 new connection applications received, adding 3.6 GW to the pipeline of projects. More than 50% of this capacity are battery energy storage projects planned for Queensland.
Twenty projects representing a combined 4.9 GW, including 687 MW of solar and 3,575 MW of batteries, received application approval during the three months to December.
Four projects, with a combined 600 MW capacity, commenced operating at full output during the quarter. Among those projects were the 200 MW / 400 MWh Rangebank battery energy storage system and the 76 MW Girgarre Solar Farm (76 MW), both in Victoria, and the 129 MW Tailem Bend 2 solar-plus-storage project in South Australia.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.









By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.