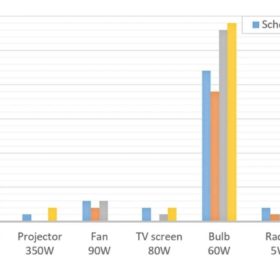
PV product prices resume downward trend, says TrendForce
TrendForce says polysilicon will be 3.2% cheaper in March than in February. This will lead to lower wafer, cell and module prices and will effectively spur installation demand.
Philippines launches tender for 25 MW solar plant
The Bases Conversion and Development Authority (BCDA) of the Philippines is seeking proposals for the lease of a 37-hectare area for solar deployment in Tarlac province.
Trina Solar unveils TOPCon solar panel series for rooftop PV
Trina Solar says its new TOPCon solar panel combines a double-glass design with n-type technology. Its efficiency ranges from 20.8% to 22.3% and the power output is between 415 W and 445 W.
Tongwei unveils 21.7%-efficient shingled solar panels for residential PV
Tongwei is offering six versions of its monofacial monocrystalline panels, with power outputs ranging from 400 W to 430 W and power conversion efficiencies between 20.1% and 21.7%.
Survey shows 34.3% failure rate for residential inverters over 15 years
The Bern University of Applied Sciences in Switzerland has published the initial results of a survey on the durability and performance of residential PV inverters and power optimisers over a 15-year period. They found that more than 65% of the inverters did not present yield-relevant faults by their 15th year of operation.
Photovoltaic-thermal system based on PCM cooling
Malaysian researchers have developed a system that can absorb heat from PV modules and transmit it to a nanofluid, in order to transform it into thermal energy and use it for different applications. The panels have an overall efficiency of 89%.
AC vs. DC in residential buildings equipped with solar-plus-storage
Scientists in Sweden have compared AC and DC topologies in PV-powered buildings using battery storage. They have found that DC distribution systems can achieve energy savings when they are combined with solar-plus-storage systems.
Solar may cover the world’s electricity demand with 0.3% of its land area
An international research group claims that raw materials and land availability do not present a real barrier for a global energy system with solar at its centre. They said that forecasts for PV growth should not have their axis on utility-scale power plants and instead consider vertical PV, agrivoltaics, and floating PV as the source of future big market volumes.
Acen Renewables starts building 360 MW of utility-scale solar in Philippines
Acen Renewables, a Manila-based developer, is building two solar plants in the provinces of Pangasinan and Zambales.
Second-life batteries might beat new ones on solar LCOE in remote locations
UK scientists have discovered that second-life batteries could provide a lower levelised cost of electricity (LCOE) than conventional batteries in school buildings equipped with PV in East African schools. They said the cheapest system configuration uses either 7.5 kW or 10 kW of solar with 20 kWh of storage.