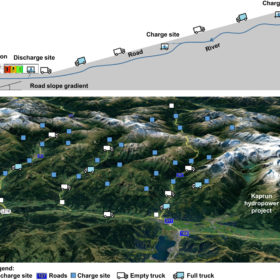
Storing hydropower via regenerative braking in electric trucks
An international research team has proposed the use of water from high-altitude rivers and regenerative braking in electric trucks to store electricity for reuse in power networks, or for transport purposes.
China’s first salt cavern for compressed air energy storage goes online
Huaneng Group has finished building a 300 MWh storage project in Changzhou, in China’s Jiangsu province. The state-owned company has already started operating the facility, which is situated in a salt cavern.
Trina Solar’s pathway to TOPCon
Trina Solar will eventually start selling TOPCon and heterojunction products, even though it built its first large-scale TOPCon project four years ago. The company says it is now making progress on TOPCon module production, despite supply chain issues.
Upcycling silicon waste from end-of-life solar panels into thermoelectrics
Researchers in Singapore have developed a new technique in which polycrystalline silicon is pulverised into powder and pelletised into ingots. The process relies on spark plasma sintering to dope the silicon with germanium and phosphorus.
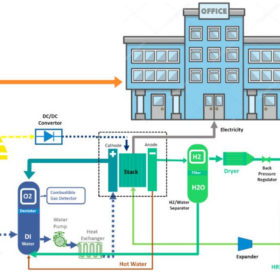
Cost comparison between lithium batteries, fuel cells, reversible solid oxide cells as storage for off-grid rooftop PV
Scientists in the United Arab Emirates have looked at how off-grid rooftop PV could be combined with batteries, fuel cells or reversible solid oxide cells for energy storage. The modelling assumed a typical commercial building in Los Angeles.
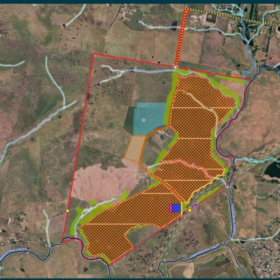
Lightsource bp to build 150 MW fishery solar farm in Taiwan
UK solar specialist Lightsource is developing a 150 MW solar park at a fishery in Budai, in Taiwan’s Chiayi county. Construction is expected to commence in June 2023.
Smarter E products at a glance
pv magazine summarises the products we covered at the recent Smarter E exhibition, in the first of a series of reports on all of the new releases from the annual trade fair in Munich, Germany.
Heat-storage building material to passively cool PV systems, batteries
German researchers have developed a new shape-stabilised phase change material with the ability to store up to five times more thermal energy than commercially available phase change materials (PCMs).
Hanwha Q Cells to build US solar module factory, expand cell capacity in South Korea
Hanwha Q Cells plans to build a 1.4 GW solar panel factory at an undisclosed location in the United States. It has also announced plans to expand its cell capacity to 5.4 GW in South Korea. CEO Justin Lee spoke to reporters at the Smarter E event about the company’s plans and current supply chain issues.
Vertical PV system for green rooftops
Norwegian startup Over Easy Solar AS is launching a vertical PV system for rooftop applications at this year’s Smarter E in Munich, Germany.