WA’s largest solar farm changes hands as SUN Energy rises
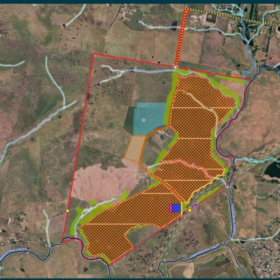
Indonesian solar PV developer SUN Energy has announced itself in the Australian market, revealing it will purchase the largest solar farm in Western Australia as part of its bold ambition to become a major player in the APAC renewable energy market.
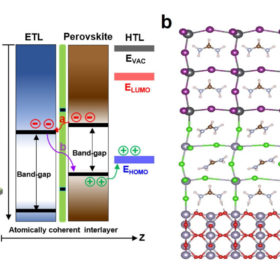
Korean researchers achieve 25.8% efficiency for single junction perovskite solar cell
The record efficiency was obtained thanks to an interlayer placed between the electron-transporting layer and the perovskite layer, which eliminated the need for passivation. The cell was also able to retain around 90% of its initial efficiency after 500 hours under standard illumination.
Will China’s ‘double carbon’ and ‘dual control’ policies drive demand for solar?
Factories suffering from rationed grid electricity could help drive a boom in on-site solar systems, and recent moves to mandate the retrofitting of PV on existing buildings could also lift the market, as analyst Frank Haugwitz explains.
Sunday read: Indonesia’s largest floating PV project – under the surface
The 145 MW Cirata floating PV project achieved financial close in August. The developers claim that the array, which covers 200 hectares of the water’s surface, is an example of transferring new technology that will pave the way for Indonesia’s solar industry and enable the setting of new policies.
Saturday read: Supplying across, through APAC market segments
One year on from its spinoff from SunPower, cell and module maker Maxeon Solar Technologies is looking to supply both “across and through” the solar market segments in the Asia-Pacific region. Chris O’Brien, the vice president of APAC for Maxeon, says that the region is set to grow in importance among PV marketplaces, with opportunities on the home, business and free field.
Big modules head for standardisation
PV manufacturing giant Trina Solar says it has agreed with other industry players on a set of standard dimensions and other technical specifications for PV modules utilising 210mm wafers – the largest currently available on the market. The manufacturer says it expects the China Photovoltaic Industry Association to formally release the standard before the end of October.
Sun Cable names ‘global experts’ to deliver massive solar+storage project
Singapore-based Sun Cable has unveiled a powerhouse line-up of international engineering and advisory companies to help it deliver the world’s biggest solar PV and battery energy storage project being developed in Australia’s remote far north.
Report finds co-located hubs key to battery industry competitiveness
A report from Australia’s Future Battery Industries Cooperative Research Centre which analysed the development of battery hubs in the U.S., Germany and Japan, has found that co-location and cooperation between industry and government were key to hub success. For Australia to play the same game, it will have to leverage its wealth of resources, and clean up its act along the way.
Sun Cable customer exits as energy price rises take toll
The world’s biggest solar PV and storage project has suffered a setback after a Singapore electricity retailer which had lined up to be a foundation customer for the renewable energy generated by Australia’s $26 billion Sun Cable project announced it will cease operations amid a record-breaking spike in electricity prices.
EDF Renewables invests in Vietnamese PV rooftop market
The French energy group has invested an undisclosed sum in Vietnam’s SkyX Energy. The goal is to install 200 MWp of C&I PV rooftop capacity in the country.