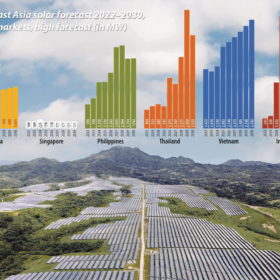
BayWa’s lessons from expanding into Southeast Asia
In recent years, global renewables developer BayWa re has been turning its attention to the Asia Pacific, expanding into Southeast Asia. Junrhey Castro, the company’s director of solar distribution in Southeast Asia, sat down with pv magazine Australia to discuss its experiences in the emerging markets of the Philippines, Thailand, Malaysia, and Vietnam.
SA renewable hydrogen export project gets green light
South Australia will launch exports of green hydrogen to Indonesia later this year with works commencing on a multi-million-dollar production facility being developed in the northern suburbs of Adelaide.
Indonesian utility kicks off tender for 100 MW floating solar plant
PT PLN Nusantara Power has launched a tender for a floating PV project that will likely be built at a dam on the island of Java, Indonesia.
ReNu completes capital raise to progress Australian, Indonesian green hydrogen projects
Queensland-based ReNu Energy has announced “firm commitments” for a capital raising of $4.5 million (USD 3 million) which it says will progress its green hydrogen projects in both Brighton and Launceston in Tasmania, as well as in Indonesia’s Riau Archipelago.
ReNu explores green hydrogen deal with 3.5 GW solar project developers
Australian independent power producer ReNu Energy has signed a deal with the developers of a proposed 3.5 GW solar-plus-storage facility in Indonesia to explore the potential large-scale production of green hydrogen for supply into Southeast Asia and beyond.
Sun Cable to help unlock Indonesia’s $170 billion green industry opportunity
Sun Cable is seeking to develop the world’s biggest intercontinental solar and storage project, and has now inked a deal with the Indonesian government that could unlock more than $170 billion (USD 115 billion) in renewable energy generation and transmission operations in the archipelago.
Indonesia may add 66 GW of solar by 2030, says IRENA
The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) says that solar could become the backbone of Indonesia’s energy system by 2030. However, the nation’s own expectations are still far off from IRENA’s scenarios.
Weekend read: Southeast Asian interconnection
While near neighbours, the electricity generation of the countries of Southeast Asia couldn’t be further apart. Indonesia burns locally mined coal, Malaysia has reserves of oil and gas, while populous Singapore, Vietnam, and the Philippines, depend on fossil fuel imports. They could all benefit from increased solar imports, but higher grid capacities and interconnection are key for an opportunity to unlock the power of the sun.
IRENA highlights solar critical to ASEAN energy transition
Indonesia will have to get to work installing more than 24 GW of solar this year – and every year – if the region is to achieve the 2.1 TW to 2.4 TW of photovoltaics the International Renewable Energy Agency has estimated it will require to achieve a net zero carbon energy system by 2050.
Singapore regulator issues fresh appeal for clean power
Singapore’s Energy Market Authority has already attracted proposals for 1.2 GW of renewable electricity, to be generated in four southeast Asian nations, and wants to raise that figure to 4 GW by 2035.