MIT, NREL researchers develop 40%-efficient thermophotovoltaic cell for grid-scale thermal batteries
The device is described as a heat engine with no moving parts that is able to produce power from a heat source of between 1,900 to 2,400 C. This concept is known as thermal energy grid storage (TEGS) and consists of a low-cost, grid-scale storage technology that uses thermophotovoltaic cells to convert heat to electricity above 2,000 C.
US body cuts PV forecast 46% due to anti-circumvention investigation
The latest update to the Solar Energy Industries Association’s (SEIA) survey for solar workers and companies shows drastic outcomes for the industry if tariffs are imposed on countries under investigation.
Photovoltaics vs. nuclear power on Mars
Solar might be more efficient than nuclear energy to supply power for a six-person extended mission to Mars that will involve a 480-day stay on the planet’s surface before returning to Earth, according to new US research.
Battery fire at Salt River Project in the US
Fire crews in Chandler, Arizona, sent robots into a building at the Salt River Project where a 10 MW battery was smouldering.
PV in the circular economy: modelling tool helps predict flow of solar materials
PV ICE uses the latest data from the solar industry to model the flow of PV materials over the next several decades, helping to predict the effects of different market trends, technological developments, and government policies.
Natural hydrogen: how the potential wellspring works and why companies are pouncing
With its promise of cheap, easy ‘god molecules’ flowing inexhaustibly from the ground, it’s no wonder natural hydrogen is piquing interest. Sometimes referred to as ‘gold’ or ‘white’ hydrogen, Avon McIntyre, executive director of HyTerra, an Australian company in the space, told pv magazine Australia natural hydrogen projects should have smaller carbon footprints than sprawling green hydrogen plays and, moreover, would be ready quicker. Enticing as it sounds, unknowns remain.
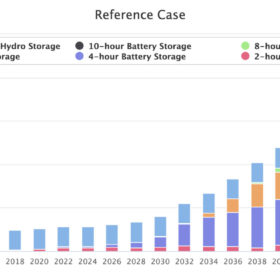
Storage projections for 2050
The US National Renewable Energy Laboratory’s (NREL) final report on the future of storage presents “key learnings” from a series of six in-depth studies.
MIT-backed startup develops polymer-based batteries for stationary storage
The device is based on a standard, two-electrode electrochemical cell containing conductive polymers, a carbon-graphene hybrid, and a non-flammable liquid electrolyte. The battery cells were tested to perform for 12,000 cycles at 100% depth of discharge.
AI method learns from experienced staff on perovskite solar production lines
Academics from MIT and Stanford who have posited a new production method for perovskite solar cells have also developed a machine learning system which benefits from the experience of seasoned workers – and they’ve posted it online for anyone to use.
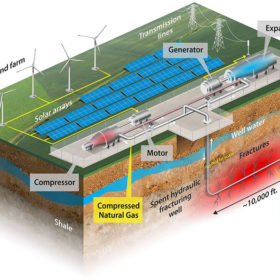
Storing renewables in depleted oil and gas wells
US researchers have proposed the use of hydraulically fractured oil and gas wells to store renewable energy via compressed natural gas, with the levelised cost of storage potentially coming in at US$70/MWh and US$270/MWh. They said wells could also be used to store other renewable gases such as carbon dioxide or hydrogen in the future.