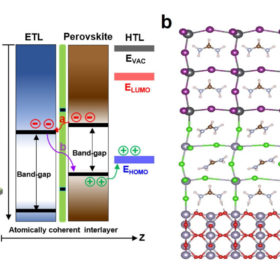
Korean researchers achieve 25.8% efficiency for single junction perovskite solar cell
The record efficiency was obtained thanks to an interlayer placed between the electron-transporting layer and the perovskite layer, which eliminated the need for passivation. The cell was also able to retain around 90% of its initial efficiency after 500 hours under standard illumination.
Weekend read: Australia’s “massive” hydrogen storage potential
Underground hydrogen storage seems to be coming up a lot lately, and with the burgeoning hydrogen industry needing somewhere to store itself, it’s not hard to understand why. One of the countries with the best credentials for the future hydrogen economy is Australia. A newly published report has quantified the country’s “massive opportunity” for underground hydrogen storage.
Saturday read: Supplying across, through APAC market segments
One year on from its spinoff from SunPower, cell and module maker Maxeon Solar Technologies is looking to supply both “across and through” the solar market segments in the Asia-Pacific region. Chris O’Brien, the vice president of APAC for Maxeon, says that the region is set to grow in importance among PV marketplaces, with opportunities on the home, business and free field.
Large-scale renewable uptake to help Rio Tinto’s brand rebuild
Mining giant Rio Tinto has been on the back-foot since its destruction of 46,000-year-old sacred indigenous sites last year, costing one chief executive his job and one country a timeless piece of its cultural heritage. Along with the impacts of Covid-19 and stock price decline, the company is seeking to rebuild its brand with improved emissions reduction targets, which will see multi-gigawatt solar and wind installations.
Big modules head for standardisation
PV manufacturing giant Trina Solar says it has agreed with other industry players on a set of standard dimensions and other technical specifications for PV modules utilising 210mm wafers – the largest currently available on the market. The manufacturer says it expects the China Photovoltaic Industry Association to formally release the standard before the end of October.
Insight Australia 2021, fully charged
Insight Australia 2021 took place on October 12th. Its wide range of speakers and Australian focus attracted many to watch the event live and participate in the insightful Q&As. For those that weren’t able to join us but are at all interested in the performance and safety of battery energy storage in the energy transition, the recording is now available.
New tracker design for agrivoltaics
Spanish company Axial Structural is introducing a new type of tracker for agrivoltaic installations. The product can be adapted to various ground conditions and gradients, with programmable to optimise light and shade for different crops in different climates.
Strong potential for inorganic perovskites
Scientists in the United States have developed a method to compare the performance and number of defects in different perovskite cell materials. Based on simulations and work with prototype materials, the group finds that all-inorganic materials have higher potential efficiency than their more widely researched organic-inorganic counterparts.
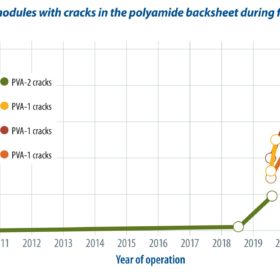
Sunday read: To replace or repair
Backsheet chalking, especially of polyamide backsheet films, doesn’t take long to lead to cracks and then safety shutdowns. Sometimes, though, the period may be much longer or shorter than expected. Assessing the risk and whether on-site repairs offer a long-term solution is currently a topic of strong debate within the PV industry, as Cornelia Lichner from the pv magazine Deutschland team reports.
Saturday read: Powerful equation to expand C&I
Big rooftop PV systems on factories, warehouses and public buildings need not be limited by ownership issues nor local grid capacity, claims Australian innovator EleXsys Energy. The company is maxing out an Ikea in Adelaide, Australia, with solar and storage. And it claims its smart technology can allow the same to be done elsewhere.