From pv magazine global
The ability to identify small defects in perovskite solar cells will mark a crucial step towards commercialization of the technology.
Although it is widely acknowledged perovskites are susceptible to instability, not much is known about the nature of the defects which cause such problems and how they affect solar cells.
Approaches to the issue have included ‘healing’ defects through carefully managed exposure to heat and light, using a potassium solution to limit the ion movement caused by such defects and inserting extra layers into cells.
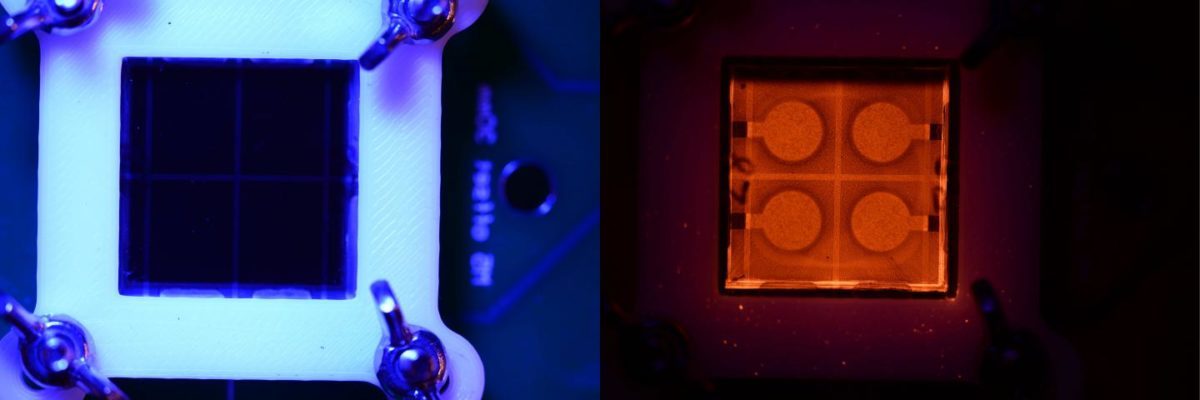
Now, researchers in Australia and China have developed a luminescence camera approach to detect such defects. The international group comprises academics from the Australian Research Council’s Center of Excellence in Exciton Science; Monash University, in Melbourne; government agency the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization; and the Wuhan University of Technology, in China.
Test runs
The Sino-Australian group said it had conducted successful test runs on batches of small cells. “Using light modulation to find these flaws is a quick and robust way to solve the problem – and one that should work on any level of production,” stated the group in results published in Nano Energy and on the ScienceDirect website.
The luminescence technique could be used to optimize perovskite solar cell development and scaled for automated process control of the promising technology, the researchers claimed. “The technique permits the rapid identification of a range of different macroscopic defects and quantifies the impact on … local series resistance.”
Perovskites remain a hot candidate as a potential PV material. Researchers in Germany used high precision photoluminescence to observe a perovskite solar cell and detect where the material emitted light in response to a laser. With the technique, the scientists were able to determine which areas and defects caused the biggest efficiency losses in the planar, pin-type perovskite cells they worked on.
A group led by Cambridge University discovered adding a simple solution of potassium to the ink solution had the effect of ‘healing’ defects in metal-halide perovskite films and immobilizing ion movement.
Researchers from leading European and U.S. universities found defects in crystalline perovskite structures could be permanently healed through careful exposure to light and humidity.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.








By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.