From pv magazine Global
Promising better module efficiencies, aesthetic appearance, flexibility in terms of device shape and size, as well as eliminating soldering and therefore lead from PV production, shingled solar module layouts have been around for a while, and are gaining ground commercially particularly in rooftop and BIPV markets.
Now, scientists at Germany’s Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE have worked with equipment supplier M10 Industries AG to demonstrate a new type of shingled layout for modules, and its applicability at industrial scale. The approach, which the two companies have dubbed ‘Matrix Shingle Technology’ (MST), places cell shingles offset from each other, similar to how bricks are laid in a wall. The creators claim this approach allows better occupation of the entire module area, leading to improved efficiency and shading tolerance, and an aesthetically pleasing homogenous appearance – according to Fraunhofer ISE, the matrix shingled technology will produce that perform between 2% and 6% better than a conventionally connected half cut cell module layout.
In work presented at last month’s EU PVSEC conference, the group found that its MST approach also leads to much better tolerance of partial shading, since current can flow around the shaded areas of the module. This could make the modules particularly suitable for building, or even vehicle, integrated solar. “Matrix shingle modules are predestined for integrated applications, especially in building façades,” says Achim Kraft, head of group Interconnection and Encapsulation at Fraunhofer ISE. “Particularly in building integration, maximum area utilisation, shading tolerance and appealing aesthetics are important.”
Straight to scale
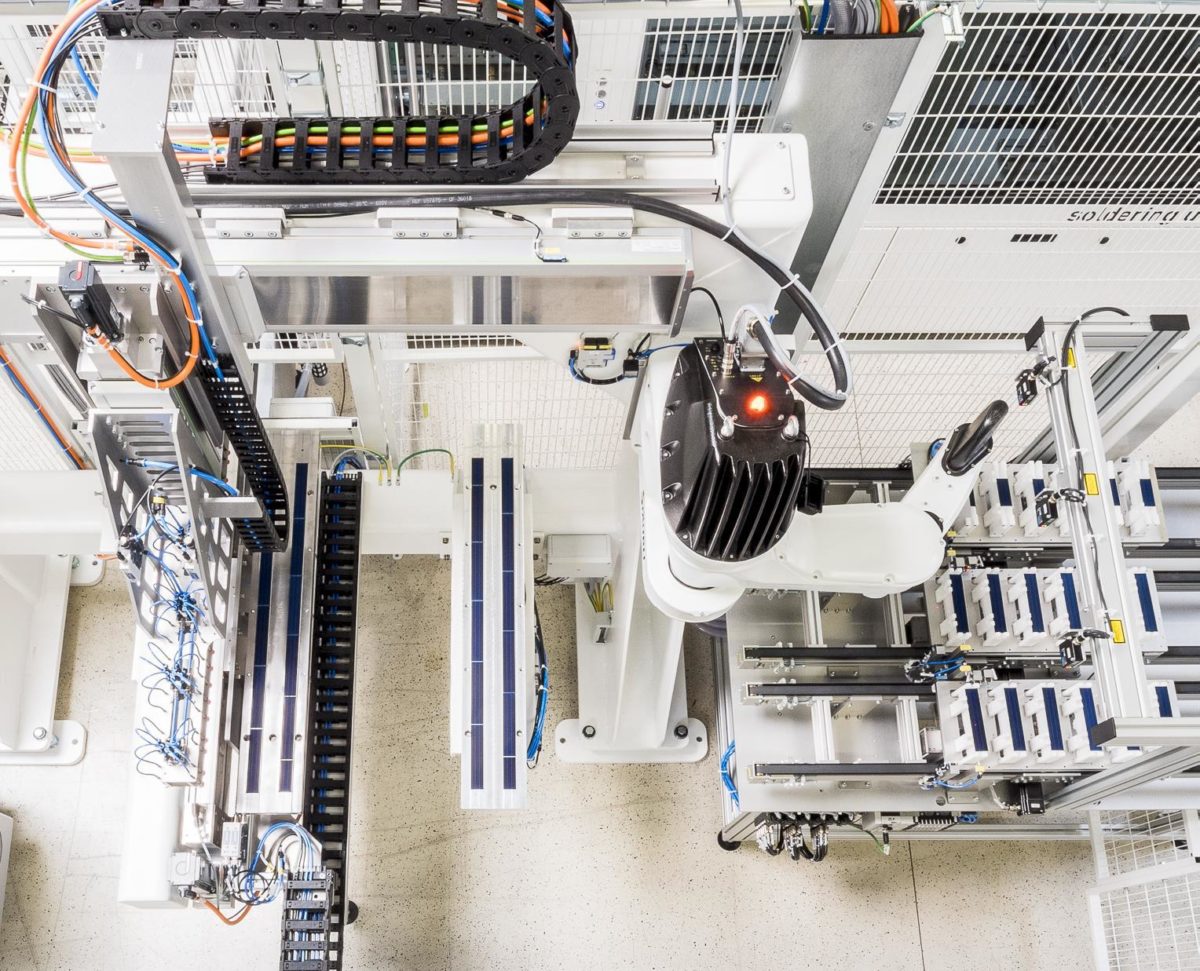
Having proven the potential of MST modules in various applications, Fraunhofer ISE worked with equipment supplier M10 Industries to demonstrate how the modules could be produced at scale. “The matrix approach has enabled us to implement a completely new machine concept. Our system has a much higher throughput than classic shingle stringers and is in no way inferior to conventional stringers in terms of megawatt output,” explained Phillipp Zahn, CEO of M10 Industries AG.
The prototype, set to be demonstrated at the Intersolar Europe Restart beginning tomorrow in Munich, can process 12,000 cell shingles per hour, and can be integrated into conventional module lines. Fraunhofer says it took only seven months to develop the tool, and that it has a prototype machine in up and running in Freiburg, and available for further testing.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.








By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.