According to a report from Geosciences Australia, Australia produces half the world’s lithium, is the second-largest producer of cobalt and the fourth-largest producer of rare earths, but China still dominates critical minerals and metals markets.
In March and on the back of straining relations between China and Australia, the Australian Government committed more than $240 million to critical minerals projects in a bit to end the country’s reliance on China and cement its place in the rapidly growing global electric vehicle and battery markets.
This week battery minerals innovator Lava Blue was awarded a grant of $5.2 million from the Federal Government’s Critical Minerals Accelerator Initiative to support the development of Lava Blue’s processes for refining critical minerals used in the lithium-ion battery supply chain.
Lava Blue’s managing director Michael McCann said the grant was a significant one which would contribute to a $12 million Queensland project over the next two-and-a-half years.
“The grant will allow Lava Blue processes to be applied to recovery of a number of valuable minerals from vanadium pentoxide processing waste, including high purity alumina and potentially magnesium and residual vanadium,” said McCann. “The outcome will be to greatly improve the economics of vanadium recovery and provide new supplies of high purity minerals into global battery supply chains.”

Image: Geosciences Australia
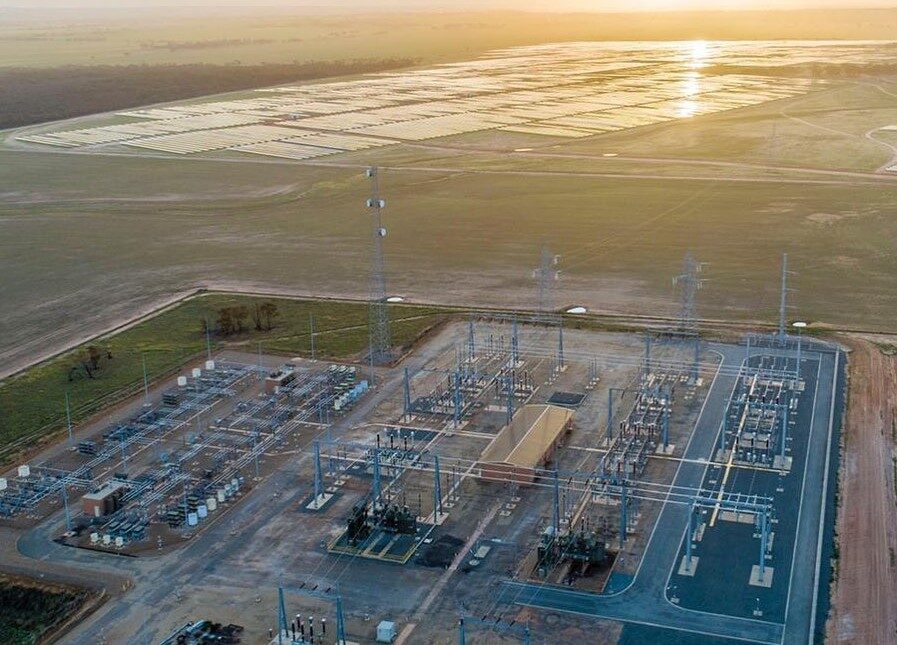
Along with Lava Blue’s research partner, the Queensland University of Technology, the project will see the scale-up of processes for recovery of high-purity minerals at the Lava Blue Centre for Predictive Research into Specialty Materials at Redlands Research Park in Brisbane.
High purity alumina (HPA) is used in the separator between battery anode and cathode.
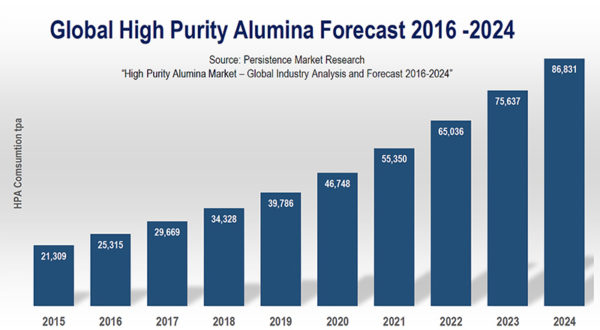
Image: Lava Blue
“Battery minerals are not industrial metals,” McCann continued. “The high degrees of processing control required for materials to feed into battery manufacturing are at a totally different level to normal mineral processing. However, Australia is rapidly developing the capacity to produce battery materials and help drive the massive historical transition to a carbon-constrained, renewable energy future.”
Lava Blue’s chairman, Sylvia Tulloch, said battery minerals and energy metals are needed over the next two decades “so that we can displace energy services currently supplied by around five billion tonnes of coal and 36 billion barrels of oil every year.”
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.









If the development of rare earths is not good, or even indiscriminate mining will not only cause huge losses to the national economy, but also cause great damage to the entire ecological environment, especially after mining, refining, and recycling rare earths if the environment is not properly carried out management, the impact on the environment will be very serious.
Large-scale mining of rare earths has a devastating impact on the environment, and large doses of rare earths can cause acute poisoning after entering the human body. The main symptoms are: vomiting, diarrhea, difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, generalized convulsions, etc., which may lead to diffuse peritonitis, peritoneal Adhesion, bloody ascites, liver opacity and swelling, focal pulmonary hemorrhage and other pathological phenomena.
Large-scale mining of rare earths has a great impact on the environment, and we should still focus on protecting the environment.
One of the most serious hazards is the mildly radioactive slurry tailings from the rare earth elements thorium and uranium. In addition, toxic acid is a necessary auxiliary material in the process of refining rare earth elements, and improper handling will lead to extensive environmental damage. A series of environmental problems, including soil erosion, landslides, ground cracks and subsidence, destruction of fertile fields, eutrophication of water sources in mining areas, and heavy metal pollution, will follow.
Rare earth is not soil, but a very important mineral resource. The mining of rare earths will bring great pollution to the ecological environment. Excessive mining of rare earths can cause ecological damage. Rare earth mining is extremely damaging to the environment and vegetation. With the massive felling of surrounding trees and the stripping of topsoil, the mountain vegetation will suffer irreparable damage wherever it goes. Due to the low content of rare earth minerals, the mining damage to land and vegetation has caused serious soil erosion. If it encounters rain erosion, it is easy to cause water pollution. Rare earth mining and processing projects pollute the environment. During the extraction and processing of rare earths, the discharge of harmful waste water, waste residue and waste gas is very serious, including a large amount of ammonia, nitrogen, sulfate, chloride ions and radioactive substances in waste water. Moreover, these contaminations remain underground for a long time. These heavy metals or harmful elements will enter rivers or groundwater bodies under the action of rain wash. Once groundwater resources are polluted, residents’ health and ecological environment will be seriously affected, and the consequences will be unimaginable.
The issue of radioactive contamination is one of the factors most blamed on the production of rare earths by many national and international environmentalists. The extraction and separation of rare earth ore needs to consume a large amount of sulfuric acid or liquid alkali, and these sulfuric acid or liquid alkali after the extraction will cause serious pollution to the environment.
Excessive exposure to rare earth elements can cause damage to the human body. The heavy metal elements contained in the rare earth itself will cause allergies if it is in direct contact with the human body for a long time. The refining process of rare earths is complicated, and other substances that are harmful to the human body are easily brought into the refining process, which will cause irreversible damage when they come into contact with human skin.
With the current technology used in rare earth mining, there is no good way. At present, the in-situ leaching process is widely used, which can minimize the damage to the mountain surface and vegetation, but there is no authoritative analysis and test results for the damage to the groundwater and the internal geology of the mountain. In addition, the more mining processes are pool leaching and heap leaching, because the damage to the mountain geological environment is serious.
The accumulation of rare earth elements in the body and their toxic effects, the harm of rare earth agricultural applications to the ecological environment and human health. Long-term low-dose intake of rare earth elements can accumulate in the liver, leading to changes in liver morphology and pathological tissue, liver cell damage, and liver metabolic disorders resulting in fatty liver.
With the current technology used in rare earth mining, there is no good way. At present, the in-situ leaching process is widely used, which can minimize the damage to the mountain surface and vegetation, but there is no authoritative analysis and test results for the damage to the groundwater and the internal geology of the mountain. In addition, the more mining processes are pool leaching and heap leaching, because the damage to the mountain geological environment is serious.
Investors shouldn’t just mean making money! The originally clear river water is now filthy. Although it is only a small rare earth factory, it has caused great harm to people. The water source has become a problem, the air pollution is serious, and some hidden questions are still unknown. When will it suddenly come in the future, such as rare harmful substances that can cause infertility and cancer, maybe such lesions will only manifest in the next few decades!
The accumulation of rare earth elements in the body and their toxic effects, the harm of rare earth agricultural applications to the ecological environment and human health. The long-term low-dose intake of rare earth elements can accumulate in the liver, resulting in changes in liver morphology and pathological tissue, hepatocytes Injury, liver metabolism disorder causes fatty liver.
The water source has become a problem, the air pollution is serious, and some hidden questions are still unknown.The accumulation of rare earth elements in the body and their toxic effects, the harm of rare earth agricultural applications to the ecological environment and human health.
Unlike other mineral resources, rare earths will be concentrated in a large amount in a certain area, and rare earths are scattered on the surface, so if you want to mine rare earths, you must develop a large area of land and stones, which will cause serious damage in the process. It is very polluting, and although some rare earths have no radiation themselves, they emit radioactive dust and leave radioactive waste during the refining process.
The extraction and separation of rare earth ore needs to consume a large amount of sulfuric acid or liquid alkali, and these sulfuric acid or liquid alkali after the extraction will cause serious pollution to the environment. The large amount of waste water and waste residue produced during the extraction of ion-adsorbed rare earth ores have seriously damaged the local soil and water sources.
The large amount of waste water and waste residue produced during the extraction of ion-adsorbed rare earth ores have seriously damaged the local soil and water sources.It is very polluting, and although some rare earths have no radiation themselves, they emit radioactive dust and leave radioactive waste during the refining process.
Rare earth mining once used the pool dipping process, like shaving a head, to remove the topsoil and vegetation on the mountain to mine rare earths, which caused irreparable damage to the mountain vegetation.
A large amount of wastewater generated from leaching, acid precipitation and other processes is rich in pollutants such as ammonia nitrogen and heavy metals, which seriously pollute drinking water and agricultural irrigation water.
Due to the extremely low grade of rare earth ore, the traditional heap leaching and pool leaching process produces about 2,000 tons of tailings per ton of rare earth oxides produced. The production process is energy-intensive, and improper handling can lead to air, water and soil pollution.
Rare earth elements in nature are usually not single, but mixed together. Such properties make rare earth exploration, mining, and smelting difficult and costly.
The refining and processing projects of rare earths cause pollution to the environment. During the process of refining and processing rare earths, the harmful waste water, waste residue and waste gas discharged by these enterprises have not been treated in time, and the pollution is very serious, which contains a large amount of ammonia, The pollution of nitrogen, sulfate, chloride ions and radioactive substances exceeds the standard by several times or even dozens of times.
Studies have shown that if rare earth elements are ingested in low doses for a long time, they can accumulate in the liver, resulting in liver morphological and pathological changes, liver cell damage, and liver metabolic disorders, resulting in fatty liver; and agricultural rare earths with a dose higher than 2mg can also pass through the placenta. The barrier causes DNA damage in hepatocytes and developing red blood cells.
The precious rare earth metals are purified, they are not radioactive themselves, but what is left is a thick liquid containing toxic chemicals and low-level radioactive waste.
The most harmful refiners in refining rare earths are those that break chemical bonds. The rare earths in the ore form tight chemical bonds with various harmful substances, especially the radioactive thorium. Breaking this chemical bond requires extremely high concentrations of sulfuric acid in the tons.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced. Rare earths contain 17 chemical elements, including lutetium, scandium, and yttrium. For most people, these chemical elements are very unfamiliar, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin.
The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
Thorium and uranium associated with rare earths are highly radioactive and are the main raw materials for nuclear weapons. Although bastnaesite is considered to be less radioactive, this is only relative to monazite, and there is still the possibility of radioactive contamination in both mining and refining.
Reports with research conclusions confirm that rare earth elements are non-essential trace elements in the human body. Lanthanum ions are similar to calcium ions, and have a high affinity for human bones. They may replace calcium ions in bones, which will inevitably affect the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in bones.
Thorium and uranium associated with rare earths are highly radioactive and are the main raw materials for nuclear weapons. They may replace calcium ions in bones, which will inevitably affect the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in bones.
Although bastnaesite is considered to be less radioactive, this is only relative to monazite, and there is still the possibility of radioactive contamination in both mining and refining.Long-term low-dose exposure or intake may have adverse consequences on human health or metabolism in the body.
Improper mining planning of rare earth resources and uncontrollable production technology lead to disordered production, waste of resources and environmental damage.
Non-market-oriented factors in the production and circulation of rare earths lead to inflated prices or violent fluctuations, declining benefits, weak follow-up applications, and market degradation.
Due to the lack of proper control of the source of rare earth mining, illegal mining and processing of rare earth mines, as well as exporting and smuggling rare earth products that circumvent the quota system have become the norm.
Rice fields and streams are often damaged by runoff such as strong acid from open-pit rare earth mining sites, which are often run by violent organized crime gangs.
The public generally questioned that Australia regarded Malaysia as a “low-level radioactive nuclear waste storage place”, otherwise, why did it not process locally.
The development of the Lynas rare earth processing plant prohibits or re-evaluates existing hazardous projects and ensures that all projects strictly comply with the principles of the “Earth Charter”.
In order to collect rare earth mines, Lynas destroys soil and water, cuts down forests, destroys farmland, grabs water, grabs land, and pollutes the land with strong acid. All areas where rare earth mines are produced eventually face unreusable land, landslides, and residents’ health. influences.
Rare earth ore is one of the associated radioactive minerals, which not only contains the required rare earth ore components, but also has mineral resources with natural radioactive substances higher than the specified level. Especially in the case of increasingly stringent environmental quality requirements, the general pollution control standards lack pertinence, and their application in the rare earth industry has gradually become insufficient.
The rare earth industry, measured by its production scale, is an industry that pollutes the environment more. Because there is no pollutant discharge standard for the characteristics of the rare earth industry, the management of pollutant discharge of rare earth industrial enterprises and the environmental impact assessment, design and completion acceptance of construction projects, etc., have been implementing comprehensive pollutant discharge standards, and their application in the rare earth industry has gradually increased. Inadequate highlighted.
With the rapid development of rare earth industry, characteristic pollutants such as ammonia nitrogen and thorium dust emitted from rare earth production have not been effectively controlled. Therefore, it is urgent to formulate pollutant emission standards suitable for this industry according to the characteristics of the rare earth industry.
Because there is no pollutant discharge standard for the characteristics of the rare earth industry, the management of pollutant discharge of rare earth industrial enterprises and the environmental impact assessment, design and completion acceptance of construction projects, etc.
The rare earth industry, have been implementing comprehensive pollutant discharge standards, and their application in the rare earth industry has gradually increased. Inadequate highlighted.The rare earth industry, measured by its production scale, is an industry that pollutes the environment more.
Rare earth especially in the case of increasingly stringent environmental quality requirements, the general pollution control standards lack pertinence, and their application in the rare earth industry has gradually become insufficient.Therefore, it is urgent to formulate pollutant emission standards suitable for this industry according to the characteristics of the rare earth industry.
They may replace calcium ions in bones, which will inevitably affect the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus in bones.Although bastnaesite is considered to be less radioactive, this is only relative to monazite, and there is still the possibility of radioactive contamination in both mining and refining.
Rice fields and streams are often damaged by runoff such as strong acid from open-pit rare earth mining sites, which are often run by violent organized crime gangs.
With the current technology used in rare earth mining, there is no good way. At present, the in-situ leaching process is widely used, which can minimize the damage to the mountain surface and vegetation, but there is no authoritative analysis and test results for the damage to the groundwater and the internal geology of the mountain.
The accumulation of rare earth elements in the body and their toxic effects, the harm of rare earth agricultural applications to the ecological environment and human health . In addition the damage to the mountain geological environment is serious.
There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases.
Rare earths contain 17 chemical elements, including lutetium, scandium, and yttrium. For most people, these chemical elements are very unfamiliar, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
Rare earths contain 17 chemical elements, including lutetium, scandium, and yttrium. For most people, these chemical elements are very unfamiliar, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.
In the smelting and separation of rare earth, a large amount of fluorine-containing toxic exhaust gas and ammonia nitrogen wastewater are produced.There are 17 kinds of chemical elements in rare earth, and long-term contact is relatively harmful to the skin, too much dust, and easy to get occupational diseases. The electrolysis of rare earths is harmful to people, and the electrolysis workshop is very harmful. The high temperature in the workshop, the large magnetic field, and the excessive dust are prone to occupational diseases.