The Australian Energy Market Operator’s (AEMO) latest Quarterly Energy Dynamics (QED) report shows that from April to June 2023, rooftop solar generation in the National Electricity Market (NEM) rose to 1,888 MW, the highest second quarter average yet recorded.
The new mark, 431 MW higher than the same time last year, was also the highest year-on-year growth yet for rooftop solar output and the second-highest recorded growth in percentage terms.
Output from grid-scale variable renewable energy (VRE) also reached a record second quarter average of 4,599 MW, up 745 MW on the same period last year. Almost half of the increase, 347 MW, came from large-scale solar with the balance from wind.
Grid-scale solar accounted for 5.5% of total generation in the NEM during the 1 April to 30 June 2023 period while rooftop PV accounted for 7.9%, a market share increase of 1.4% and 1.8% respectively.
The share of renewables might have climbed even higher if not for limits due to system strength and other network constraints. VRE curtailment increased by 20 MW from Q2 2022 with about 61 MW of generation lost for the quarter.
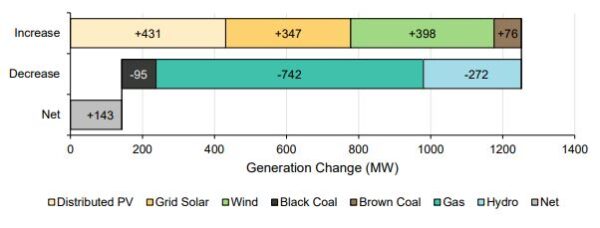
Image: AEMO
AEMO Executive General Manager Reform Delivery Violette Mouchaileh said the higher renewable output and improved generation availability had combined with less volatile market conditions to put downward pressure on wholesale electricity prices.
“Increased market share of lower marginal-cost renewables helped push down the wholesale electricity cost from Q2 2022, despite this quarter having the highest Q2 underlying demand recorded since 2016,” she said.
“In addition to increased wind and grid-scale solar output, lower thermal-coal costs and a net increase in black-coal generation availability in NSW, despite the retirement of the Liddell Power Station, helped reduce year-on-year wholesale prices.”
Total emissions in the NEM declined during the quarter to the lowest Q2 levels on record at 28.7 million tonnes of carbon dioxide, 6.6% lower than the same period last year.
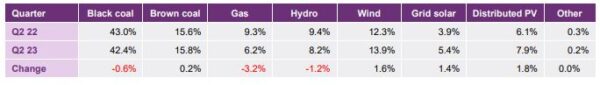
Image: AEMO
The latest edition of the QEM report has for the first time included data on the number of connection applications and capacity processed over the quarter.
AEMO said it received 16 new connection applications from projects totalling 3.9 GW of capacity in the June quarter, with 30 GW of new renewable energy projects now working their way from connection applications to commissioning.
“At the end of Q2 2023 there were 10.3 GW of plant at various stages of construction (pre-registration), compared to 6.5 GW at the end of Q2 2022,” the market operator said.
“The number of connections progressing through registration and commissioning remains relatively similar across both quarters, with 1.2 GW and 3.9 GW of plant progressing through registration and commissioning respectively in Q2 2023, compared with 1.5 GW and 5.0 GW in Q2 2022.”
AEMO noted that the construction timelines of large-scale renewable projects are being affected by the “need to refinance, long lead times for equipment, and the need to change original equipment manufacturers.”
AEMO said there had been a 63% increase in new connection approvals in the past financial year, up from 4.2 GW to 6.8 GW capacity.
The amount of plant approved for registration to commence commissioning fell by 32% to 2.4 GW. However, the amount of plant that completed the commissioning process over the year, and were approved for full operation, increased by 21% to 2.9 GW.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.









By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.