The case against gas has been highly publicised because of its greenhouse gas emissions and substantial costs.
But the government’s focus on large solar infrastructure in rural areas, away from our main centres, misses a chance to address two urgent issues at once – the need to cut emissions and to adapt to climate impacts.
Centralised versus decentralised energy systems
Centralised renewable electricity generation using large-scale hydro, wind and solar infrastructure helps to cut emissions and move New Zealand closer towards a fully renewable grid. These projects can be implemented quickly and are a positive step.
However, we must also focus on climate change adaptation. Creating more renewable electricity alone won’t help during power outages, which might become more frequent due to climate-related extreme weather events.
During Cyclone Gabrielle in 2023, almost 234,000 homes lost power, some for over a week.
Solar technologies offer opportunities to distribute electricity generation and storage by integrating power into buildings and cities. Bringing electricity generation close to where it is used helps to increase resilience during extreme weather events and other disruptions to power lines, including earthquakes.
Although large solar farms generate clean electricity at scale, they keep generation far away from where it is used. This applies new technologies in an old-fashioned way, centralising power generation in a few locations, controlled by a handful of companies.
Government policies and incentives could help to integrate solar generation into communities to create resilient places, with access to their own power during natural disasters and outages.
For instance, integrating solar panels into schools, public buildings, hospitals and homes would enhance resilience, especially for our most vulnerable populations.
While there are already some projects of this type through the New Zealand Solar Schools Project and Community Renewable Energy Fund, much more could be done. Instead of using productive farmland distant from communities, we could better utilise the many rooftops and walls available in cities.
Even though solar power’s peak generation around midday does not align with peak electricity demand in New Zealand, every small solar system connected to the grid contributes. At the national scale, the water flowing into hydro lakes could be held back in the dams to meet evening peaks in demand when solar is no longer available.
SolarZero’s virtual power plant, made up of thousands of home batteries, is already helping New Zealand get through cold snaps by feeding electricity to the grid. Photovoltaics have become significantly more affordable and there are many finance options available. But these technologies are still not accessible for many households, especially rental properties.
Policies and incentives could make it easier for everyone to afford solar-powered homes. Having public buildings with solar panels in every community would enable basic access to energy for everyone.
Potential of distributed solar power
To visualise how solar infrastructures could be distributed in cities, we use the size of New Zealand’s largest solar farm as an example.
With a total land area of 93 hectares and 63 MW of capacity, the solar plant will generate enough renewable energy to power approximately 13,000 homes. We explore how this land area could be distributed on Auckland’s rooftops.
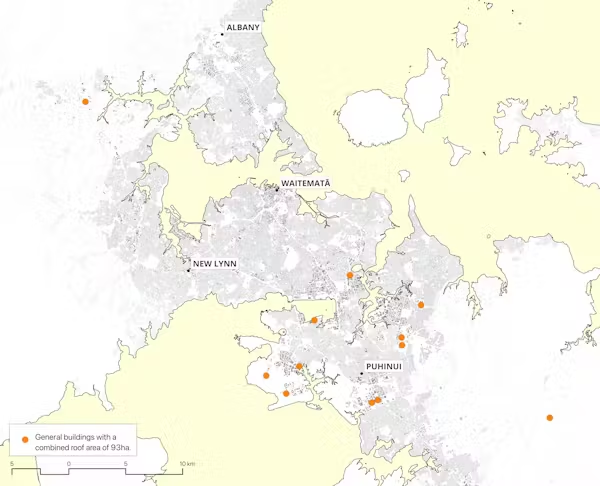
Image: Andrew Burgess, CC BY-SA
The map above applies the total land area of the solar farm to 14 of the largest building rooftops in Auckland.
The map below distributes this power more evenly to communities by utilising the rooftops of schools and supermarkets, totalling 167 buildings.
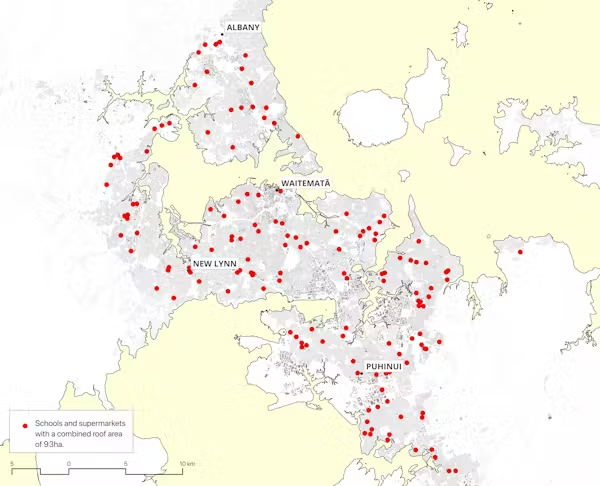
Image: Andrew Burgess, CC BY-SA
Both scenarios show how we could better utilise the space available on rooftops in our cities. The second scenario presents a higher potential of creating resilient communities due to its geographical distribution; these places could help locals during power outages.
Locally generated solar power is key to resilient, sustainable cities and New Zealand’s transition to a zero-carbon future. Decentralised renewable energy, especially building-integrated solar power, brings power generation closer to consumption.
In a country subject to multiple natural hazards, investment in solar for public buildings and homes could bring several benefits for disaster resilience and climate change mitigation.
Authors: , Lecturer in Sustainable Architecture, Auckland University of Technology; , Senior Lecturer in Architecture, Auckland University of Technology; , Associate Professor in Interactive Design, Auckland University of Technology; , Lecturer in Environmental Engineering, Auckland University of Technology; , Lecturer in Architecture , Auckland University of Technology
This article was initially published in The Conversation and is republished here under a Creative Commons Licence
The views and opinions expressed in this article are the author’s own, and do not necessarily reflect those held by pv magazine.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.








By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.