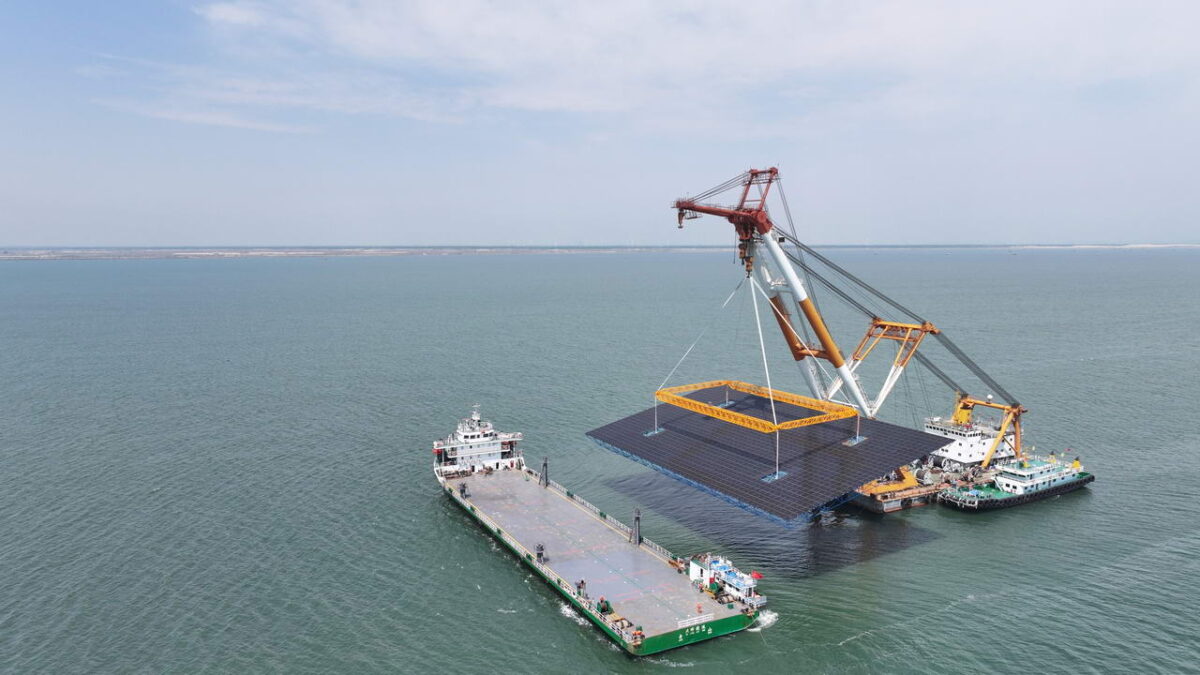
China is advancing its marine solar ambitions with a 1.8 GW offshore PV demonstration project being built in the Bohai Sea off the coast of Changli in the northeast province of Hebei. With a total investment of $3.07 billion (CNY 14.4 billion), the scheme — the first of its scale in Hebei — is being jointly developed by four central state-owned enterprises: Huadian, Guodian, Guohua Investment, and China Power Construction.
Spanning approximately 17 square kilometres of sea area and including four sub-projects, the floating solar development is scheduled for full grid connection by the end of July 2026.
According to the government of Qinhuangdao, the upper administrative of Changli, the project comprises four distinct sub-schemes:
· Huadian Changli 500 MW Pilot: AC side capacity of 460.8 MW, covering 4.68 square km, estimated annual generation of 770 GWh, with investment of CNY 3.1 billion. Uses fixed-mount structural designs.
· Guodian 500 MW Project: with investment of CNY 2.6 billion, expected annual generation of 690 GWh, internal rate of return on equity is 7.02%, to use N-type TOPCon modules and 110 kV collection lines.
· Guohua 500 MW Project: DC/AC capacity of 500/201.6 MW, deploying 620 Wp N-type TOPCon modules with 300 kW string inverters, planned for completion in November 2025.
· China Power Construction 300 MW Project: Deep-water fixed pile foundation design, largest platform sizes and greatest average water depth among the four projects, detailed technical parameters not disclosed yet.
All four sub-projects connect via submarine cables to self-built 220 kV booster stations, then feed into the Qin Hai Guang 500 MW boost station. The Huadian subproject employs 110 kV collection lines and directional drilling for submarine cables, reportedly setting national records in cable routing distance.
Construction has been proceeding since early 2025. As of August 2025, about 240 steel-pipe piles have been installed. In the coming months, submarine cable laying and equipment commissioning work will intensify.
When operational, the project is forecast to generate some 2.75 TWh annually — meeting about 49% of Qinhuangdao’s electricity demand — and reduce annual coal consumption by an estimated 840,000 tonnes, cutting CO₂ emissions by about 2.16 million tonnes each year. Local industry will benefit with the project expected to create more than 2,000 new jobs, while the green energy supply chain (marine equipment, power engineering) is projected to generate over CNY 1 billion in annual economic output.
As Hebei’s first large-scale offshore PV initiative, the Changli scheme is being positioned as a demonstration model for China’s wider marine solar strategy.
With ample shoreline resources, high solar irradiation, and proximity to load centres along the eastern seaboard, offshore PV is viewed as one of the most promising paths for clean energy expansion. Experts estimate that by 2030, marine solar could contribute more than 10% of China’s clean energy capacity growth, with cumulative offshore PV installations exceeding 100 GW.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.







By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.