Compressed-air storage for commercial applications
Israel-based Augwind has built its first 250 kW/1 MWh compressed air storage system for the collective community of Yahel, in the southern, desert part of the country. The commercial scale facility will be connected to a PV system and will be used for behind-the-meter services.
Converting coal mines into gravity-based renewable energy storage facilities
U.K.-based Gravitricity is planning to deploy its gravity-based energy storage solution at a decommissioned coal mine in Czechia. The project is part of a plan to commence a full-scale, 4-8 MW prototype scheme in a disused mine next year.
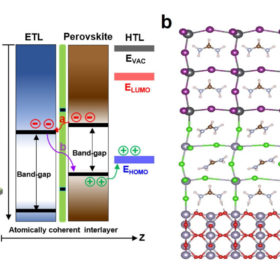
Korean researchers achieve 25.8% efficiency for single junction perovskite solar cell
The record efficiency was obtained thanks to an interlayer placed between the electron-transporting layer and the perovskite layer, which eliminated the need for passivation. The cell was also able to retain around 90% of its initial efficiency after 500 hours under standard illumination.
Risen showcases n-type solar panel with output of 700 W
The 210 mm module can reach a power output of up to 703.6 W and a power conversion efficiency of 23.08%. The result was confirmed by Germany’s TÜV SÜD.
Electro-thermal storage system for commercial applications launched
Developed by Swedish manufacturer Azelio, the system stores renewable energy in recycled aluminium and has an electrical and thermal energy output, with a total efficiency of 90 %. One unit’s storage capacity reaches 165 kWh of electrical output and on top of that thermal energy between 55-65 degrees Celsius. Its modular configuration allows the deployment of projects with a capacity of up to 100 MW.
Vanadium redox flow batteries with purported LCOS of $0.10/kWh
Singapore-based VFlowTech has secured funds to scale up manufacturing of its vanadium redox flow batteries. The company currently offers three modular products that can be scaled to multi-megawatt-hour systems.
Vietnamese manufacturer unveils PV module for agrivoltaics
Vietnamese manufacturer Irex has announced a new glass-glass solar panel with a power output of 265 W and a power conversion efficiency of 18.1%.
Panasonic launches 5 kW fuel cell system for commercial applications
The system has dimensions of 834×417×1,766 mm and weighs 205 kg including the design panel. It achieves an electrical efficiency of 56% and can be connected with a hot water storage unit.
Solar tile with 14.2% efficiency from Denmark
Dansk Solenergi ApS has developed a 13.6 kg tile that can be used for both new buildings and building renovation. The device is currently being produced in Denmark, where the company operates a 40 MW line.
New discovery could make organic PV competitive with crystalline silicon
A group of international researchers has observed how non-radiative charge recombination occurs in organic PV and claims to have identified a potential solution that could bring this solar tech closer to crystalline silicon in terms of power conversion efficiency.