Poweroad launches 233 kWh battery for C&I solar
The Chinese manufacturer said that up to 10 battery cabinets can be connected in series to reach a total storage capacity of 2.33 MWh.
University researchers develop passive solar module cooling method
Researchers in Iran developed a passive solar module cooling method using silicon carbide porous ceramic. When combined with phase change materials, the technique reportedly boosts panel performance by up to 7.4%.
Solis launches new hybrid inverters for C&I solar
The Chinese manufacturer said its new product is the world’s largest wall-mounted hybrid inverter. The series includes three models, with AC outputs of 80 kW, 100 kW, or 125 kW.
Chemitek Solar launches new antistatic soiling mitigation coating
The Portuguese company said its new anti-soiling solution lasts for at least a year. It can be applied during routine cleaning operations by mixing it directly in the cleaning water.
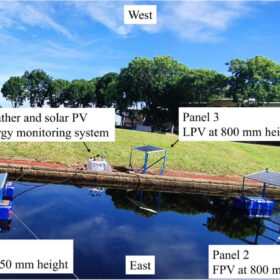
Testing reveals height benefits of floating PV
Scientists have tested the performance of floating PV panels at a height of 800 mm and 250 mm above their floating structures. Their thermal and electrical performance was compared to that of a reference land-based system and the highest panel was found to show the greatest cooling effect.
Sungrow releases modular inverter for utility-scale solar
The Chinese manufacturer said its new product uses inverter units with an output of 800 kW, of which 12 can be connected in parallel. It can work in weather of up to 52 C.
Trina debuts 5 MWh energy storage system
The Chinese manufacturer said its new utility-scale battery uses 314 Ah cells with a 15,000-cycle lifespan.
PV module recycling tech based on electrohydraulic shockwave fragmentation
An international research team has developed a new machine that utilises shockwaves to separate the different materials of a PV module. Chemical processes can be further used to extract silicon and silver. Results show the recovery of more than 99.5% of the original weight of the panels.
NT solar centre data feeds ultra-short-term PV forecasting method
Scientists utilising data gathered at the Northern Territory’s Desert Knowledge Australia Solar Centre have created a novel probabilistic model for five-minutes ahead PV power forecasting. The method combines a convolutional neural network with bidirectional long short-term memory, attention mechanism, and natural gradient boosting.
Viridian Solar launches 23.6% efficient TOPCon BIPV panel
United Kingdom-based manufacturer Viridian Solar says the new modules have a rated power output of 445 W and can reportedly guarantee a power yield of 95% after 10 years.