Australia tries to boost hydrogen competitiveness
Finance consultancy explains in a new report that the levelised cost of green hydrogen (LCOH) is well below USD 2/kg with subsidies. Using either PEM and alkaline electrolysers, green hydrogen normally has a lower levelised cost than pink hydrogen. Meanwhile, Australian authorities are trying to increase the competitiveness of the local hydrogen sector, and car companies are updating their fuel cell plans.
Report warns of risks for Australia in global green hydrogen race
The federal government is increasing its investment in green hydrogen and low-emissions steel with $50 million in research and development funding to help progress the technologies as a new report warns that Australia must act quickly or risk being left behind in the race to become a renewable energy superpower.
Adelaide company granted license to explore hydrogen storage in SA’s underground salt caverns
South Australian technology company EntX has been granted a license to explore salt deposits along the western side of the Eyre Peninsula in South Australia for the purpose of hydrogen storage.
5 GW green hydrogen project wins bid for SA’s Eyre Peninsula
Canadian-headquartered clean energy firm Amp Energy has secured the rights to develop a green hydrogen project with up to 5 GW of electrolyser capacity on the Eyre Peninsula in South Australia. Amp has signed an agreement with iron ore miner Iron Road which owns the coastal site, including the Cape Hardy Port Precinct.
Perth-company with UWA hydrogen technology signs deal with Japan
Seeking to commercialise hydrogen technology developed by the University of Western Australia, Perth-based Hazer Group has entered into a somewhat vague agreement with Japan’s Chubu Electric Power Company and engineering firm Chiyoda Corporation.
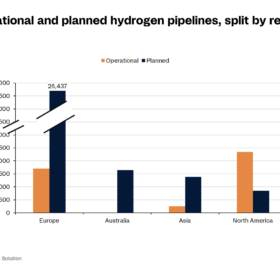
Global hydrogen pipeline projects to surge by 2035, says Rystad
Norwegian consultancy Rystad Energy says that hydrogen pipelines will be “far better” than vessels at moving hydrogen over short- and medium-range distances in the years ahead.
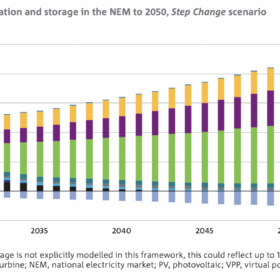
CSIRO says Australia’s storage capacity must grow tenfold, urges alternative technologies
Australia’s national science agency, the CSIRO, estimates the country could require a 10 to 14-fold increase in its electricity storage capacity between 2025-2050. It has released its energy storage report, forecasting demand in different sectors and summarising storage technologies.
CS Energy formalises plans for Queensland green hydrogen project
The Kogan Renewable Hydrogen Demonstration Plant, which is expected to produce approximately 75 tonnes of green hydrogen annually from behind-the-meter solar energy, is nearing reality after CS Energy formalised its joint venture arrangements with ASX-listed gas company Senex Energy.
Viability of ‘direct’ green hydrogen fuel production evaluated by US researchers
Rather than using solar or wind to power electrolysis, researchers are testing the competitiveness of photoelectrochemical cells to produce emissions-free hydrogen fuels.
International players bid to build SA green hydrogen plant
Plans to develop a major green hydrogen production facility near the South Australian industrial city of Whyalla has sparked global interest with the state government revealing 29 international and domestic players have signalled their interest in delivering the project.