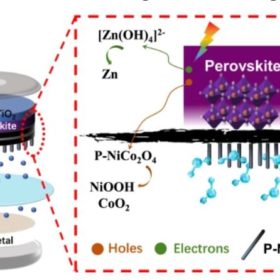
PV-powered rechargeable aqueous zinc battery
Conceived by scientists in China, the device combines an integrated carbon-based perovskite solar cell module with a rechargeable aqueous zinc metal cell. The proposed system achieved an overall efficiency of 6.4%, and a steady operation for more than 200 cycles with little performance degradation.
Sunday read: V2G driving grid changes
The uptake of EVs in the years ahead will add up to staggering battery capacity, mostly sitting idle on driveways. The two-way flow of electricity from EV batteries, known as vehicle to grid, could not only enable power systems to rely on intermittent renewables, but could also be the trump card for network operators to respond to grid disturbances. However, there are still a few catches to be worked out, as Marija Maisch explains.
Saturday read: the actual, real demand for green hydrogen
Green hydrogen is being proposed for an ever-wider variety of uses. While some of these are still a way off, others make little sense. But there are sectors where demand for green hydrogen is a reality today, writes Christian Roselund.
Solar trailer for off-grid applications
Developed by French start-up Ecosun, the trailer is equipped with 15 solar panels with output of 360 W and batteries with a storage capacity of 23 kWh. It can be used for construction sites, military camps and water pumping systems.
EleXsys targets rooftop solar increase with trial of next-gen technology
Queensland company eleXsys Energy has secured more than $450,000 to help finance a trial of next-generation technology designed to manage grid stability in low voltage areas, potentially allowing for an increase in the amount of distributed energy resources, including rooftop solar, that can be connected to the grid.
Microgrid project using vanadium redox flow battery
SDG&E and Sumitomo Electric complete a pilot microgrid project in California that successfully powered utility customers solely with energy stored in a flow battery.
High performance seawater batteries based on novel anode material
Scientists in Korea have developed an efficient synthesis route to produce a novel co-doped anode material for rechargeable seawater batteries. They developed a one-step plasma-in-liquid process to synthesise nitrogen and sulfur co-doped carbon-based anode material, which displayed great potential for seawater batteries.
Australian researchers claim solar cell efficiency record
Researchers at the Australian National University say they have set a perovskite solar cell efficiency record at 22.6%. This efficiency, however, appears to be lower than that achieved in January by a group of Swiss and Korean researchers who used quantum dots to achieve an efficiency of 25.7% in an area of 0.08cm2 and 23.3% in 1cm2.
Australian zinc-bromide batteries chosen for Acciona’s Spanish testing field
Gelion’s zinc-bromide Endure batteries will undergo commercial tests at the 1.2 MW Montes del Cierzo testing field Spanish renewable energy company Acciona Energía operates in Navarra, in the north of Spain.
Natural hydrogen exploration ‘boom’ snaps up one third of South Australia
South Australia has found itself at the heart of a 21st century gold rush, though this time for naturally occurring hydrogen. Since February 2021, 18 exploration licenses have been granted or applied for in the state by six different companies searching for natural hydrogen.