Saturday read: New applications see surge in Chinese demand
China’s project development segment is dynamic, to say the least. Having undergone significant changes toward a “subsidy-free” footing, developers are now facing requirements to integrate storage, deploy hybrid arrays, and pursue self consumption through BIPV and agrivoltaics applications, writes Frank Haugwitz, the director of the Asia Europe Clean Energy (Solar) Advisory (AECEA).
Why rooftop solar failed to find its legs in India
Poor and piecemeal implementation of net metering policies is a major roadblock for the uptake of rooftop solar system in India, according to a new report by Asian Development Bank.
Saturday read: China reaches a tipping point in 2021
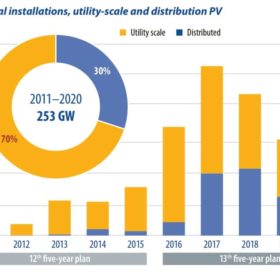
This year will be a key period in the development of China’s solar PV market. It is the first year of the 14th five-year plan, the first calendar year after President Xi Jinping announced the 2030-60 carbon emissions commitment, and the first year for utility and commercial unsubsidised projects. IHS Markit expects the solar industry in China to reach another milestone with more than 60 GW of installations this year, advancing the ground for the energy transition and the displacement of traditional energy sources to fullfill the goal of a net carbon future over the next four decades to come.
Jolywood signs megadeal with Chinese utility to supply 7 GW of household solar
Based on current market prices, the five-year contract could be worth almost $4 billion to the $1 billion company, but the TOPCon manufacturer has not publicised the price at which it will supply and install modules for its state-owned sponsor.
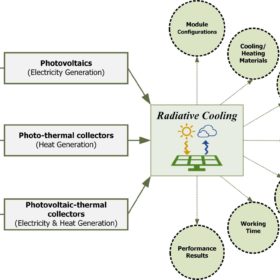
The best radiative cooling tech for PV arrays
Scientists in China have analysed the radiative cooling techniques used in combination with solar energy systems such as PV arrays, solar thermal collectors, and concentrated PV installations. They identified five major system typologies based on functionality and working time.
Big solar-plus-storage comes to Taiwan
Taiwanese module maker URE Corp is planning to link a 150 MW solar plant to a 15 MW/15 MWh storage facility.
Thai plans for 8 GWh lithium battery gigafab
The 1 GWh first phase of a planned 8 GWh lithium battery factory in Thailand is likely to be up and running during 2023.
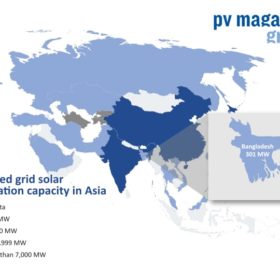
India to finance 100 MW Bangladeshi solar plant
The federal government will provide $131 million of soft loans for a $177 million, 100 MW solar park near the Jamuna river in Bangladesh’s Jamalpur district, where a second park of a similar size is being planned by Dhaka and a Chinese partner.
A different angle on perovskite defects
Scientists in China took a closer look at the role of defects in limiting the performance of perovskite solar cells, demonstrating a screening effect that could be tuned to make material defects “invisible” to charge carriers, greatly improving cell performance. Using this approach they demonstrate a 22% efficient inverted perovskite solar cell, and theorise several new pathways to even higher performance.
South Korea kicks off 2 GW PV tender
The Northeast Asian nation has included PV projects exceeding 20 MW in size for the first time in its solar energy procurement scheme. Selected projects will be awarded a fixed rate under a 20-year contract under the country’s renewable energy certificate (REC) scheme and will sell electricity to local power distributors.