Latent heat thermal storage with PV for nearly zero-energy buildings
Researchers in Italy are combining PV with latent heat thermal storage (LHTM) and other renewable energy sources to maximize clean energy consumption in buildings. The 47kW PV array and LHTM system work independently, but the scientists said that a heat pump could be used to link them.
Fraunhofer ISE reaches legal settlements with seven inverter manufacturers who infringed its patent
In 2002, the Fraunhofer ISE patented the HERIC circuit for highly efficient inverters. Since then, the institute says, it has recorded out-of-court settlements in seven patent infringement lawsuits against companies from China, Taiwan and Germany.
New investor to boost Gransolar’s Australia vision
Spanish renewables group Gransolar says backing from international financier will “supercharge” its growth plans in Australia.
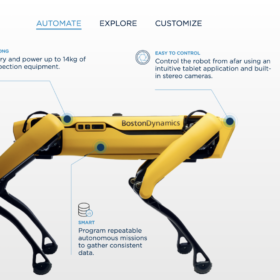
Robot dog for PV plant monitoring
Spanish renewable energy company Acciona is using a robot dog, instead of drones, to monitor a solar park in northern Chile. The device has a built-in thermal vision system that generates thermographic reports on the status of the different PV plant components, as it walks between the panel rows following a programmed route.
Large-scale storage options for compressed hydrogen
Researchers from Finland and Sweden have reviewed different ways to store compressed gaseous hydrogen, including storage vessels, geological storage, and other underground options.
New German leader proposes ‘climate club’ that would punish free riders like Australia
Germany has announced plans for a new climate alliance between the world’s advanced economies, in a move that promises to transform international climate action.
Solar trailer for off-grid applications
Developed by French start-up Ecosun, the trailer is equipped with 15 solar panels with output of 360 W and batteries with a storage capacity of 23 kWh. It can be used for construction sites, military camps and water pumping systems.
Australian researchers claim solar cell efficiency record
Researchers at the Australian National University say they have set a perovskite solar cell efficiency record at 22.6%. This efficiency, however, appears to be lower than that achieved in January by a group of Swiss and Korean researchers who used quantum dots to achieve an efficiency of 25.7% in an area of 0.08cm2 and 23.3% in 1cm2.
Australian zinc-bromide batteries chosen for Acciona’s Spanish testing field
Gelion’s zinc-bromide Endure batteries will undergo commercial tests at the 1.2 MW Montes del Cierzo testing field Spanish renewable energy company Acciona Energía operates in Navarra, in the north of Spain.
Vanadium redox flow battery to control extreme power ramps in rooftop PV
Researchers in Portugal have tested how vanadium redox flow batteries can be integrated with rooftop PV to balance the system load to ensure firm power output. They proposed a 5 kW/60 kWh battery configuration for a 6.7 kW building-integrated PV microgrid. According to their findings, the battery can be used in different energy management strategy scenarios to better complement solar photovoltaic generation.