Five trends for energy storage as global market passes 100 GW
A new report from Wood Mackenzie identifies five key trends the global research and consultancy group expects will define the energy storage industry in 2026, including supply chain restructuring and the rise of non-lithium batteries.
Musk says solar space-based AI data centres possible in two to three years
Space-based solar could power AI more efficiently than on Earth, with full-scale deployment possible in two to three years, Elon Musk says SpaceX’s Starship launch vehicle and its reusable rockets aim to sharply reduce space access costs, enabling solar-powered AI satellites and potentially large-scale extraterrestrial energy infrastructure.
‘Immediate transition to copper is technically and economically feasible’
With silver prices rising, more large solar manufacturers are expected to switch to copper for cell metallization. Radovan Kopecek of ISC Konstanz tells pv magazine that he expects the entire industry to follow. Ning Song of the University of New South Wales says a small efficiency tradeoff may be acceptable if the cost savings are significant and do not introduce new reliability risks.
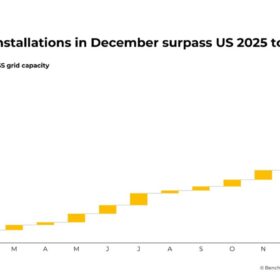
Global BESS demand jumps 51% in 2025 as installations top 300 GWh
Iola Hughes, Head of Research at Benchmark Mineral Intelligence, says 2026 is set to be another strong year for battery energy storage systems, with forecast additions exceeding 450 GWh and no material supply constraints in sight. Meanwhile, the initial impact of rising lithium prices is already visible at the cell level, but the full effect has yet to ripple through to system pricing.
From scrapheap to strategy: Exploring reuse and recycling strategies for solar mounting structures
As many PV plants approach the midpoint in their typical lifespan of 25 to 35 years, the industry faces crucial decisions about what comes next. Much of the focus so far has been on managing modules, particularly on recovering their silicon and other materials. But the conversation must also extend to mounting structures. As the backbone of all solar plants, these structures represent a significant share of material use and a plant’s embodied carbon footprint.
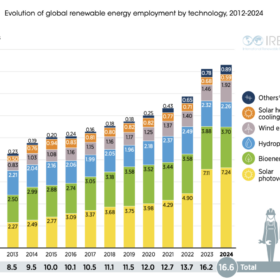
Solar accounted for 7.24 million jobs in 2024
The International Renewable Energy Agency’s annual review into employment finds solar held more than 43% of global jobs in the renewable energy sector in 2024.
Hydrogen faces ‘year of reckoning’ in 2026, says Wood Mackenzie
Wood Mackenzie’s 2026 market outlook for hydrogen expects non-biological origin hydrogen to gain momentum and ammonia crackers to reach commercial scale but predicts the Middle Eastern market to retreat and the European Union to abandon its industrial hydrogen mandates.
Solar module efficiency could exceed 35% by 2050
A new Perspectives research study on the future of the global PV supply chain outlines how module prices, performance, and lifetimes could evolve over the next 25 years. The work reflects a collaboration among leading solar research institutions worldwide. One of the study’s authors, the director of the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems, told pv magazine that solar module and cell efficiencies could exceed 35% by 2050, with panel prices expected to drop by a factor of two.
Huawei, Sungrow lead Wood Mackenzie’s inverter market ranking
Wood Mackenzie’s first-half 2025 solar inverter ranking finds the top 10 leading inverter manufacturers have a 71% global market share.
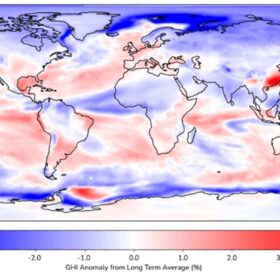
Early forecast: First half 2026 solar outlook
In a new update for pv magazine, Solcast, a DNV company, reports that early 2026 will bring mixed solar conditions globally, with strong prospects in eastern Australia and eastern China, but cloudier-than-normal outlooks for much of Europe, Asia, and parts of the United States early in the year.