Building the wind and solar farms, batteries and electricity networks we need to run our system on renewables will use a huge array of mined minerals, known as “transition minerals”.
The numbers are staggering. The International Energy Agency estimates a sixfold increase in demand for these minerals by 2040 to meet climate targets of well below 2℃ of warming. We could need 21.5 million tonnes for electric vehicles and battery storage alone.
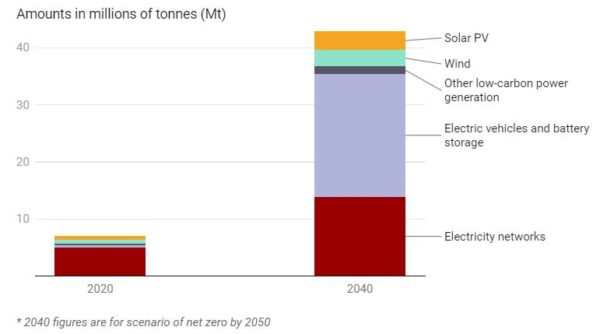
Image: The Conversation Source: The Role of Critical Minerals in Clean Energy Transitions/IEA Get the data Created with Datawrapper
Transitional minerals include metals such as lithium, cobalt, copper, graphite, magnesium and nickel. They also include rare earths like neodymium, praseodymium, dysprosium and terbium.
Currently, mining provides almost our entire supply. The scale of demand for these minerals could result in almost 400 new mines by 2035.
How can we manage demand?
We can design energy and transport systems to minimise mineral demand. Strategies include:
- reducing our dependence on cars and using smaller vehicles
- improving energy efficiency
- moving to a circular economy that makes reuse and recycling a priority.
All these changes can reduce the need for new mines.
Recycling, for example, could reduce demand for mined materials. For lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles, estimated reductions are 25% for lithium, 35% for cobalt and nickel, and 55% for copper by 2040.
This recycled content will mainly come from waste batteries. However, large volumes of lithium-ion batteries won’t start reaching the end of their lives for at least a decade. Recycling will only have a significant impact from 2035.
Six key trends in the battery #recycling market.
As uptake of #ElectricVehicles skyrockets, we look at some of the key trends in the #Lithium battery recycling and black mass marketshttps://t.co/nt703PzinW pic.twitter.com/xFisoemxfr— Earth Accounting (@EarthAccounting) June 20, 2023
If we are destined to continue mining for the minerals needed for the energy transition, how can this be done responsibly? And what exactly do we mean by responsible sourcing?
Responsible sourcing minimises the environmental, social and governance impacts and risks of mining. Key concerns include the use of child labour and forced labour, damage to the environment, impacts on Indigenous rights and cultural heritage, and corruption.
In 2011, the Australian government released guidance on sustainable mining. Historical and recent harmful impacts highlight the need for a fresh look at mining practices. In 2020, for example, Rio Tinto destroyed a 46,000-year-old Aboriginal heritage site in Juukan Gorge.
First Nations people worldwide are calling for free, prior and informed consent when mining and renewable energy developments are proposed for their land. This approach recognises the right to be consulted early in the process, informed of the impacts, and supported to take part in negotiation and making agreements. Most importantly, it includes the right to say no.
In many parts of Australia, Indigenous communities have been locked out of economic opportunities, despite mining generating enormous wealth on their Country.

Image: PKKP and PKKP Aboriginal Corporation/AAP
What does responsible sourcing involve?
How do we do things more responsibly? We need to ensure activities comply with a range of sustainability criteria. An agreed standard will mean we have information that enables us to compare the good and bad apples.
The problem is there isn’t a common approach to measuring, managing and reporting environmental, social and governance performance. Our recent research analysed the plethora of voluntary standards and certifications available to battery materials producers. No common global or Australian standard has been adopted.
Smaller mining companies also struggle with the administrative complexities of sustainability reporting and management criteria. An agreed common language for reporting and management is needed. Only then can traceability solutions, such as the Global Battery Alliance’s blockchain-enabled “battery passport”, produce trustworthy and comparable results.
Mathy Stanislaus (@MathyStanislaus) is the Interim Director of the Global Battery Alliance (@wef). Below he explains what the Battery Passport is, and how it can help reduce child labour in the DRC. #thecostofcobalt pic.twitter.com/rMmkryhUSA
— The Cost of Cobalt🇨🇩 (@thecostofcobalt) January 10, 2021
Let’s set the bar high
Our research identified the Initiative for Responsible Mining Assurance (IRMA) as one of the more rigorous standards. Its credibility is built on how it is governed. This involves six stakeholder groups: mining companies, purchasers, NGOs, affected communities, labour organisations and the finance sector.
There are still questions to be answered. How do practices in Australia measure up to the standard? And how can regulatory reform help to steer mining operations in the right direction?
A focus on environmental, social and governance practices in the Australian Critical Minerals Strategy, released last week, is a welcome first step.
Issues that must be front and centre include:
- mining impacts on water supply
- free, prior and informed consent from First Nations communities
- integrated planning for climate change impacts such as extreme weather that may affect management of mine tailings
- biodiversity protection
- mine closure planning that integrates progressive rehabilitation of ecosystems
- circular business practices to make the most of what we have.
As a leading mining nation, Australia is in a position to leverage its historical environmental leadership, show renewed responsibility and integrity, and lead by example. We can then help leave the planet in a shape that future generations will be proud to inherit.
Authors: , Senior Research Consultant, Institute for Sustainable Futures, University of Technology Sydney; , Research Principal, Institute for Sustainable Futures, University of Technology Sydney.
This article first appeared in The Conversation and is republished here with permission.
The views and opinions expressed in this article are the author’s own, and do not necessarily reflect those held by pv magazine.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.








By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.