Allied Green Ammonia (AGA) announced it has signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with Plug Power to deliver up to 3 GW of electrolyser capacity for its estimated $12.7 billion (USD 8.5 billion) green hydrogen to ammonia production facility being developed in remote East Arnhem Land in the Northern Territory.
Plug said it has also signed a basic engineering and design package (BEDP) for the 3 GW capacity project sited near the township of Nhulunbuy on the Gove Peninsula.
AGA, which will develop, own, and operate the facility, said feasibility and pre- front-end engineering design (FEED) studies for the proposed production facility have been completed and the BEDP and FEED works are expected to commence shortly.
The Perth-based company is targeting a final investment decision by the fourth quarter of 2025 with the progressive delivery of the 3 GW electrolyser supply slated to begin in early 2027. Commercial operations are scheduled to begin in the first quarter of 2029.
AGA founder and Managing Director Alfred Benedict said the MOU with Plug builds on a long list of global firms that have already signed on to build what would be one of the largest green ammonia production facilities in the world.
A process licence has been signed with Denmark-based company Haldor Topsoe for use of its ammonia production technology while a project development agreement has been signed with Spanish engineering firm Técnicas Reunidas. An interim land agreement also has been signed with local landowners, the Gumatj Corporation.
Benedict said the agreement with Plug is a critical step in the project’s development and a strong vote of confidence in the facility, which will be one of the most energy efficient green hydrogen and green ammonia projects globally.
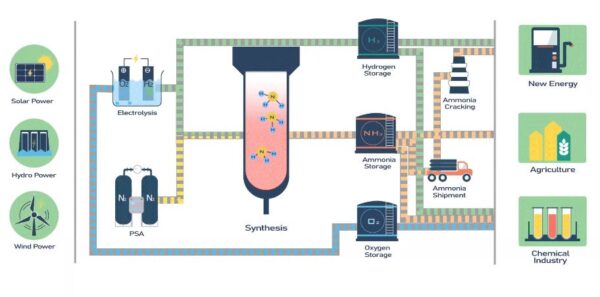
It is anticipated the project will generate 9,500 GWh per annum from as yet unidentified renewables-based sources to produce 165,000 tons of green hydrogen annually, which will be used to manufacture 912,500 tons of green ammonia per year. Production is planned to start in early 2029 at the latest.
Benedict said the project is strategically located given its proximity to expanding southeast Asian markets where demand for e-fuels continues to grow.
It would also benefit from the pre-existing infrastructure including a port and desalination plant that was established to support mining giant Rio Tinto’s bauxite mining operation, that is slated to be shut down no later than 2030, and alumina refinery which was mothballed in 2014.
AGA’s announcement follows the release of this year’s Federal Budget which will pour an estimated $8 billion into incentives over 10 years to support the production of green hydrogen.
The package includes a production tax incentive that will cost up to $6.7 billion over the next decade to support the growth of a competitive industry by providing a $2/kg incentive scheme for each kilogram of green hydrogen produced between 2027 and 2041 (less than half the U.S. incentive of $4.60/kg (USD 3/kg).
The budget also provides $1.3 billion in new funding for the Hydrogen Headstart program that provides financial support for large-scale renewable hydrogen projects, adding to the original $2 billion allocated.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.









By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.