Solar technology manufacturing major Trina Solar has submitted a development application for the proposed $400 million (USD 272 million) Kemerton battery energy storage system (BESS) to be constructed near Harvey in Western Australia’s (WA) southwest.
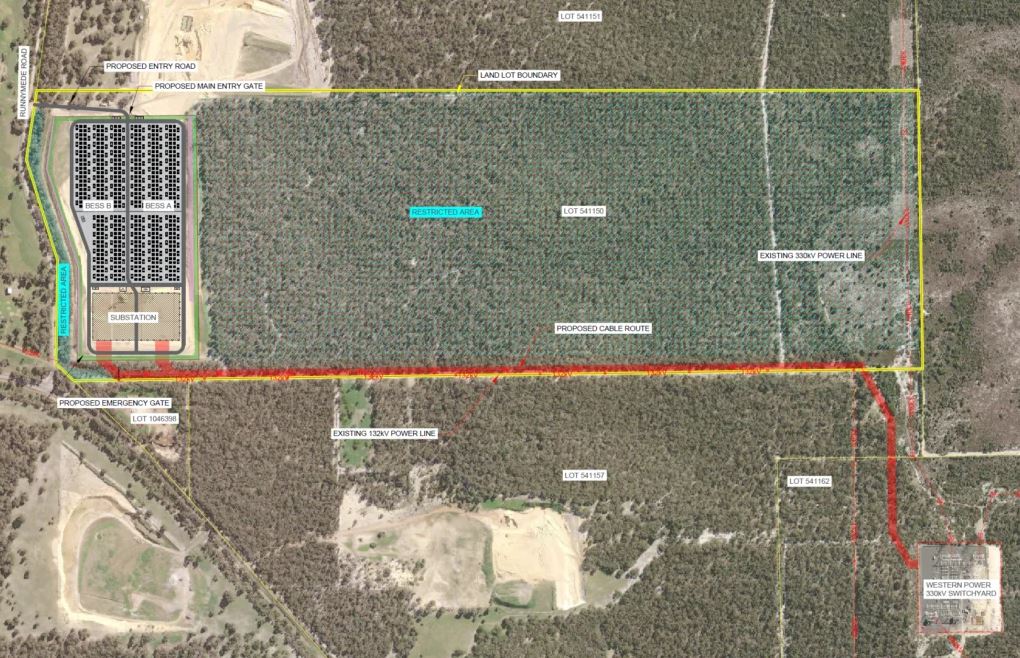
The planned battery facility will have a capacity of up to 660 MW with four hours of storage and is to be built on a 19-hectare site located in the Kemerton Strategic Industrial Area near Bunbury, about 200 kilometres south of Perth.
Trina said the site, in close proximity to existing 330 KV infrastructure including transmission lines and the Kemerton terminal station, had been identified through a rigorous selection process.
“This terminal station represents a strategic connection point in the SWIS (South West Interconnected System),” Trina said in its supporting documents, adding that the proposed battery “will be capable of supporting grid stability through grid-forming technology and facilitating renewable energy integration, such as wind and solar resources.”
“The KBESS represents a cutting-edge renewable energy facility that aligns perfectly with the state’s vision for a cleaner, more sustainable future,” the proponent said.
In its application, Trina said the grid-forming energy storage technology being utilised by the Kemerton BESS will ensure “a secure and reliable electricity supply by providing system strength and inertial response to replace that lost due to the retirement of coal plants in the region and by firming the supply of intermittent renewable energy sources within the state to ensure that there is a reduced risk of capacity shortfall.”
Construction of the Kemerton BESS is expected to commence in Q3 of 2026 with the facility to take up to 24 months to build. The project will include up to 800 battery energy storage system containers, 200 inverters with MV transformers, and four high-voltage substations.
In addition to the Kemerton BESS, Trina is also developing the 500 MW / 1,000 MWh Kiewa Valley battery energy storage project in northeast Victoria, and the 270 MW / 540 MWh Augusta BESS in South Australia.
The standalone battery energy storage projects form part of the company’s broader development strategy that is to deliver more than 6.5 GW of utility scale renewable projects, including solar and hybrid projects, across the country by 2027.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.








By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.