‘Least-cost’ model for compressed air energy storage
Stanford University researchers have created a model to assess how much compressed air storage capacity might be needed for the deep decarbonisation of power systems, while compensating for the variability of wind and solar-based power systems. They applied the model to California’s energy system and found that compressed air could be very competitive on a dollars-per-kilowatt-hour basis.
VPP participation appears overblown with questionable fleet inclusions
Virtual Power Plants, or VPPs, are relatively mature in Australia due to the country’s high penetration of, and familiarity with, distributed energy resources. But claims of VPP success and participation may be overblown, with a considerable gaps between the numbers some platforms are claiming and the realms of possibility.
Investigating load scenarios for grid-forming inverters
A consortium led by the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems (ISE) will test grid-forming inverters at a large-scale PV facility in southern Germany. The aim of the first tests is to examine the performance of the devices under real operating conditions, stress factors, and typical stress profiles.
Sparc reports ‘exceptional’ results in sodium-ion battery project
Australian battery technology innovator Sparc Technologies is reporting “exceptional” results in its campaign to develop sustainably sourced hard carbon material for the production of anodes for the nascent sodium-ion battery market.
Viability of ‘direct’ green hydrogen fuel production evaluated by US researchers
Rather than using solar or wind to power electrolysis, researchers are testing the competitiveness of photoelectrochemical cells to produce emissions-free hydrogen fuels.
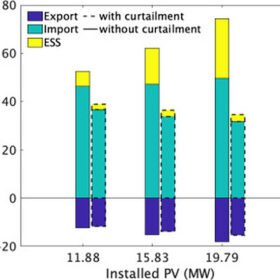
Solar curtailment vs. storage
Swiss researchers have looked at whether storage could be cheaper than curtailment in medium-voltage distribution networks with significant amounts of PV capacity. They considered storage costs, operational costs, grid constraints, electricity costs, PV generation models, and loads.
New global solar capacity additions hit 191 GW in 2022, says IRENA
Global renewable capacity increased by 295 GW last year, bringing the world to a cumulative installed capacity of 3,372 GW, according to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA).
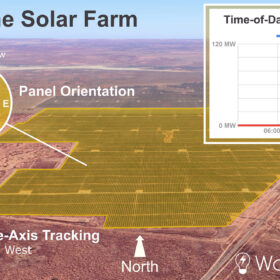
Why capacity factor is an increasingly simplistic way to compare solar farm performance
Capacity factor is often discussed when evaluating and comparing the efficiency and performance of solar farms. However, looking just at this metric can be misleading as it ignores many underlying technical and commercial factors, as solar farm specifications almost never align for a simple apples-to-apples comparison.
Global study highlights potential of floating solar
An international group of researchers has calculated the potential for floating solar across the world. The results show a generation potential of 9,434 TWh per year across 114,555 global reservoirs, with 30% of their area covered. The United States leads with 1,911 TWh per year of potential, with Australia coming in 8th, with 210 TWh per year.
The politics of an unsettled energy transition
University of Sydney researchers Sophie Webber and Gareth Bryant highlight the key challenges of land, labour and finance in achieving a renewable energy transition in Australia.