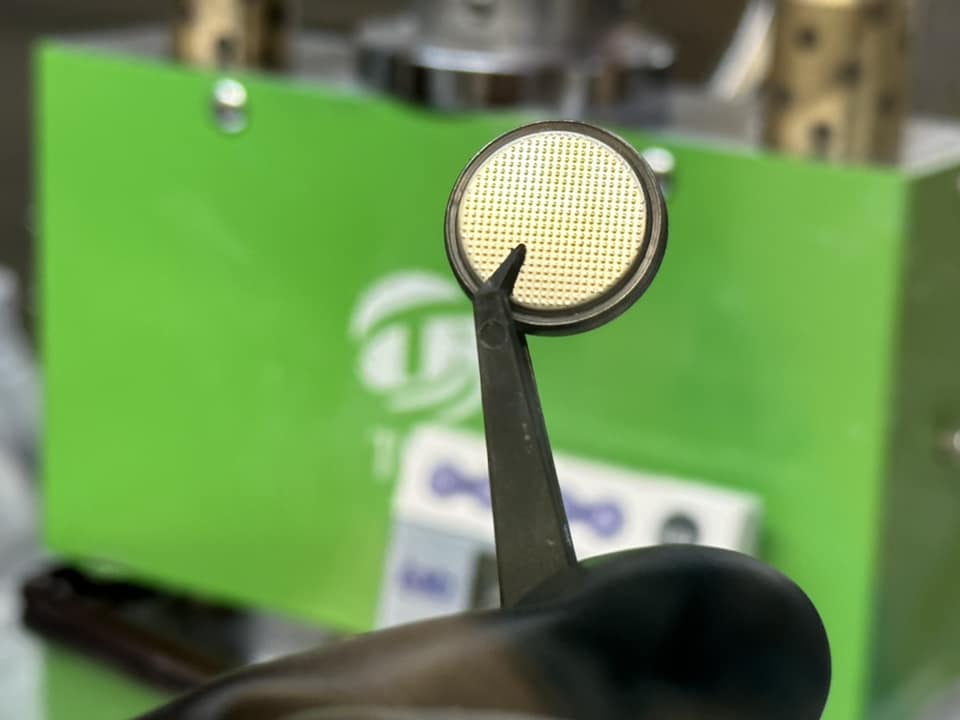
Graphite has served as the dominant anode material for much of the early phase of lithium-ion battery chemistry but Brisbane-based AnteoTech is now seeking to commercialise its silicon anode technology which it says delivers a performance-enhancement trifecta – increasing battery capacity, decreasing charging times, and lowering costs.
AnteoTech Head of Clean Energy Technologies Business Manuel Wieser said the company’s proprietary AnteoX additive reinforces battery binders and helps maximise the performance of silicon-containing anodes by increasing the energy density, cycle life, and cost efficiency of batteries for electric vehicles (EVs), energy storage systems, and consumer electronics.
“The industry has experienced incremental improvements in energy density but… improvements that can be attained by the use of conventional anode and cathode materials are approaching their limit,” Wieser said. “Which is why we are seeing a spectrum of material and cell chemistry innovations that are pursued by the major cell manufacturers and automotive OEMs [original equipment manufacturers].”
Wieser said after pure lithium, elemental silicon has the highest theoretical energy storage capacity for lithium ions. In comparison to graphite, silicon can store up to 10 times more lithium ions by weight and up to three times more by volume.
“This means that the more silicon is incorporated into the anode the smaller and lighter the anode and, consequently, the full battery becomes,” he said. “This translates into battery cells that can store the same amount of energy in a smaller volume or more energy in the same volume.”
“Ultimately, this translates into electric vehicles with additional driving range without having to change the dimensions of the battery pack or, in wearable devices or consumer electronics, that last longer between charges.”

Image: AnteoTech
Wieser, who is scheduled to present on the future direction of lithium-ion battery chemistry at the Energy Next conference to be held in Sydney on July 18 – 19, said the shift to silicon also offers benefits when it comes to charging times.
“Given that the electrode reduces in thickness with an increase in silicon content, silicon anodes can also enable fast-charging performance for electric vehicle applications due to the shorter lengths ions and electrons have to travel through the electrode thickness,” he said.
Wieser said the anode electrode thickness of pure silicon anode designs can easily reduce up to three times compared to conventional graphite-based anodes.
Silicon does however have drawbacks, including that it expands by up to 280%, given its ability to store more ions compared to conventional graphite materials, and Wieser said if not addressed appropriately this leads to rapid capacity fade and battery life degradation.
The high cost of silicon is also an issue, but Wieser said the key differentiator of AnteoTech’s silicon anode approach is that it uses industrial silicon which is more than eight times cheaper on a dollar per kWh basis compared to other silicon materials in the market.
“AnteoTech’s silicon anodes contain up to 90% of silicon, where mass-produced cells currently contain silicon at levels that are lower than 10%,” he said. “In essence, the company provides the smarts to make this crude silicon work extraordinarily well by pairing the anode design with proprietary technologies.”
Wieser said AnteoTech has already demonstrated pure silicon anode battery cells that achieve 500 full charge and discharge cycles while retaining 90% of the battery’s initial capacity with the full silicon anode product being in late-stage development.
AnteoTech is currently looking to scale up production of AnteoX with a first manufacturing facility being established in Brisbane which will be able it to produce 20,000 litres in its first full year of operation.
The move comes after AnteoTech earlier this year signed separate non-binding agreements with Swiss-based battery developer Wyon AG and Trinseo Europe, a division of global plastics manufacturing conglomerate Trinseo.
The partnership with Trinseo aims to improve the binding processes in silicon anode battery construction, while the partnership with Wyon seeks to develop and test AnteoTech’s anode design to deliver a material improvement in the performance of Wyon’s battery cells.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.








1 comment
By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.