Evergen, Solar Services Group partner to drive large-scale VPP deployment
Solar and battery optimization technology provider Evergen and solar battery provider Solar Service Group have joined forces to connect thousands of residential batteries across Australia. By delivering significant benefits to consumers, the joint venture hopes to boost the uptake home batteries nation-wide.
Shared solar switched on at Melbourne apartment block
A microgrid installed on an apartment block in Melbourne will provide clean and affordable electricity to 52 low-income households. It is the first site of Ovida’s Community Energy Hubs project, which will deliver shared solar PV and batteries to more multi-tenanted buildings in the city.
ARENA funds Wattwatchers toward more consumer empowerment
The Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) is set to fund Australian energy technology company Wattwatchers to the tune of $2.7 million. The funding will aid the development of a consumer-facing energy data hub, ‘My Energy Marketplace,’ another step forward in consumer energy empowerment.
Edify Energy solar farms to use AI trading platform for energy market participation
The Australian renewables developer has deployed AMS’ AI-backed trading platform across a 438 MW portfolio of utility-scale solar farms in Queensland and Victoria. The technology will help navigate the increasing price volatility and maximize returns in the National Electricity Market.
New app helps charge Tesla EVs when electricity is greener and cheaper
With its app already present in Belgium and the Netherlands, start-up Jedlix is introducing smart charging in France. The solution enables Tesla drivers to optimize their charging strategy.
Vicinity completes Australia’s largest solar car park installation
Australian retail property major Vicinity Centres has delivered two solar carparks at its shopping centers in South Australia, one of which is the nation’s biggest at 3.2 MW. One of the centers also has a solar battery trial underway and both will have EV charging stations as of next year.
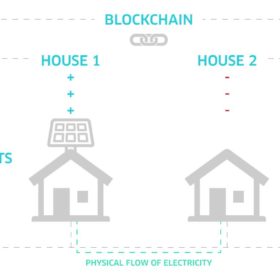
Sonnen, Natural Solar join SA blockchain-enabled virtual power plant
Western Australian energy trading technology company Power Ledger and wholesaler energy retailer Powerclub have teamed up with German battery manufacturer sonnen and solar and battery installer Natural Solar to launch their virtual power plant pilot in South Australia. The project is the first large-scale commercial rollout of blockchain technology for solar energy trading in Australia.
AEMO calls for submissions on VIC-NSW interconnector expansion
The Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) has published a report with TransGrid looking to assess the viability of an expansion to the NSW-VIC interconnector, a much-needed infrastructural upgrade. AEMO is seeking submissions on the interconnector and other transmission investment options.
ATCO begins blending green hydrogen into gas network
The Clean Energy Innovation Hub has hit a major milestone as ATCO started testing blending renewable hydrogen into the on-site natural gas network in Jandakot.
Charging an electric vehicle in 10 minutes
Scientists from Penn State University have developed a self-heating battery for electric vehicles which is said charge in only 10 minutes at 60 degrees Celsius.