PV in the circular economy: modelling tool helps predict flow of solar materials
PV ICE uses the latest data from the solar industry to model the flow of PV materials over the next several decades, helping to predict the effects of different market trends, technological developments, and government policies.
Solar greenhouse trials perform better than expected, proving commerciality company says
The results from solar glass company ClearVue’s greenhouse trials at Murdoch University have found the company’s product performed better than predicted overall, demonstrating both strong power generation and thermal value.
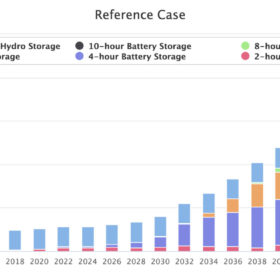
Storage projections for 2050
The US National Renewable Energy Laboratory’s (NREL) final report on the future of storage presents “key learnings” from a series of six in-depth studies.
Australia’s critical minerals inventory boosted significantly in 2020, vanadium up 24%
Australia’s inventories of critical materials for batteries have seen major increases recently, with vanadium up 23%, lithium up 8%, rare earths up 4% and platinum group elements up 185% in the year to December 2020.
Mapping Australia’s battery mineral waste ‘gold mine’
To encourage industry to consider the battery mineral opportunities currently sitting in neglected heaps around the country, Geoscience Australia and its partners are developing an Atlas of Australian Mine Waste. The public database hopes to highlight the opportunity in reprocessing mining waste for new markets.
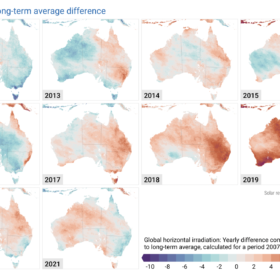
Australia’s increasingly turbulent irradiance laid bare in decade of mapping
Solar data company Solargis has released 10-year solar performance maps showing Australia’s massive variations in irradiance and the impacts of extreme weather patterns and events.
Radiative cooling for PV modules – challenges and prospects
A group of international scientists has investigated the potential use of radiative cooling in PV systems, in a newly published review focusing on challenges and opportunities for the passive cooling technology.
CSIRO to invest $50 million in storage tech of tomorrow
The CSIRO will invest $50 million in four new programs to drive critical breakthroughs in electric vehicle batteries and creating storage solution which could “mimic pumped hydro.”
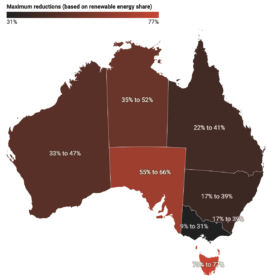
How climate-friendly is an electric car? It all comes down to where you live
If you’re thinking about buying an electric vehicle, whether due to soaring fuel prices or to lower your greenhouse gas emissions, where you live can make a huge difference to how climate-friendly your car is.
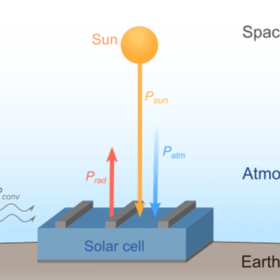
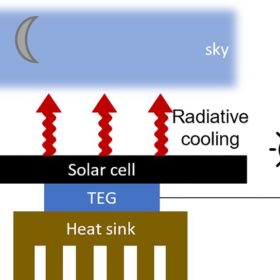
Radiative cooling-based solar cell with 50 mW/m2 of generation at night
Stanford University scientists have developed a solar cell with 24 hours of power generation via an embedded thermoelectric generator, which extracts power from the radiative cooler at night. Extra daytime power from excess heating comes from the cell itself.