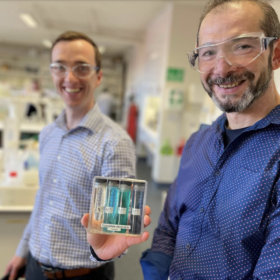
Pumped heat energy storage seeks to demonstrate commercial readiness
Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) has commissioned a first-of-its-kind pilot plant pumped heat energy storage demonstration facility with tech from US startup Malta. Its 10-150+ hour energy storage technology is said to be applicable in a range of grid-scale applications.
SunDrive achieves 26.41% efficiency with copper-based solar cell technology
Australian solar technology company SunDrive continues to impress with its copper-based solar cell technology, achieving 26.41% efficiency for a full-size silicon cell using mass-production compatible heterojunction technology.
Enphase partners with Home Connect to manage home appliances from single app
Integrated clean home energy and smart appliances platform lets users run appliances on battery-stored solar energy in pre-determined time frames.
Hydrogen bromide flow battery for large-scale renewables storage
Dutch startup Elestor has secured funds to bring its hydrogen bromide (HBr) flow battery technology closer to commercial production. It said the system could achieve a levelised cost of storage below US$0.05/kW.
Weekend read: Dawn of virtual transmission
Quick and versatile, batteries are providing a growing number of services to homes, businesses, and on the grid. Electricity network operators are beginning to adopt grid-scale batteries, with the initial applications potentially opening the way for renewable energy to flow more freely and across larger distances than ever before.
Vanadium flow battery electrolyte focus of three year industry-backed study
West Australian company Technology Metals Australia, or TMT, will work with the government-backed Future Battery Industries agency to develop enhanced electrolytes for vanadium redox flow batteries. TMT will provide both the feedstock for the research as well as funding and hopes to eventually leverage the project’s findings.
Energy Renaissance moves ahead with battery giga-factory
Australia’s first lithium-ion battery giga-factory is expected to begin operations soon with battery manufacturer Energy Renaissance announcing the successful completion of a $1.47 million pilot program designed to develop and test its manufacturing processes, systems and plant design.
H2X goes to market with hydrogen electricity generators
Clean energy start-up H2X Global has notched a major milestone with the first of its hydrogen-powered generators – built to replace traditional fossil-fuel fired gensets and provide green electricity for emergency supply and off-grid operations – released to the Australian market.
WA company expands R&D to test technology it claims boosts lithium-ion battery capacity by 30%
West Australian company Altech Chemicals has expanded its research and development laboratories to test how its “breakthrough” alumina-coated silicon for lithium-ion battery anodes performs for higher powered applications.
Wollongong university green hydrogen breakthrough team awarded grant for cell extracting hydrogen in methane
The University of Wollongong professor behind the capillary-fed electrolyser breakthrough now being commercialised by Hysata has received grant funding to develop a cell for extracting pure hydrogen from methane mixtures.