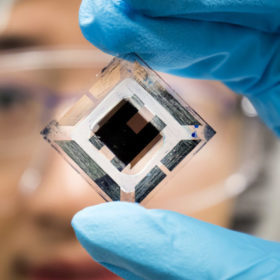
Solar tile with 14.2% efficiency from Denmark
Dansk Solenergi ApS has developed a 13.6 kg tile that can be used for both new buildings and building renovation. The device is currently being produced in Denmark, where the company operates a 40 MW line.
New discovery could make organic PV competitive with crystalline silicon
A group of international researchers has observed how non-radiative charge recombination occurs in organic PV and claims to have identified a potential solution that could bring this solar tech closer to crystalline silicon in terms of power conversion efficiency.
How one chemical engineer is channeling Australia’s plentiful PV into hydrogen-derivative renewable fuels
Rose Amal arrived in Australia from Indonesia 38 years ago to study at UNSW. Now her leadership and research are contributing to a new sustainable economy for Australia and clean fuels for energy-hungry industries.
Feeling the industrial heat: carving a path to green thermal
Beyond curtailment of abundant solar and wind output lies a giant sponge of industrial need. Engie Impact is determined to connect the dots.
Comparing new solar module formats
JA Solar published data comparing its own modules, based on the 182mm wafer format, with others utilising the larger 210mm size over a six month period in field testing. The data show that the smaller of the two formats reached an average daily energy yield almost 2% higher. According to JA Solar’s analysis, the higher currents produced by the 210mm modules led to higher resistance, and more energy lost as heat.
HDF to construct baseload power plant using green hydrogen, plans Australia expansion
The project includes a solar park coupled with what HDF Energy claims is the “largest green hydrogen storage of intermittent electricity sources” at 128 MWh. Importantly, the company also simultaneously announced expansion plans into Australia, saying its hydrogen technology will soon be available here, adding that it has “projects already in development for Australia”.
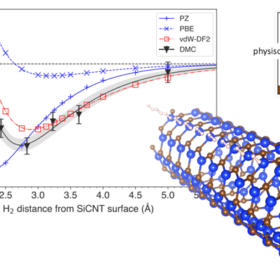
Storing hydrogen with silicon-carbide nanotubes
Storing hydrogen in carbon nanotubes and other nanostructures is still far from reaching commercial maturity. A Japanese research team, however, has developed a new simulation technology that may help better estimate the energy needed to favour the ideal interaction between hydrogen and its storage material.
APsystems reveals dual microinverter it claims to be most world’s most powerful
The 97%-efficient microinverter has a power output of up to 960 VA and APsystems claims it is the most powerful dual microinverter in the world.
China develops tech to detect module faults in all weather and lights
The system combines software that applies a modulated electric current to the PV panels and an indium-gallium-arsenide (InGaAs) photodiode detector that takes a sequence of images of the panels. According to its creators, the proposed technique works with any lighting conditions and in all weather.
Solar-plus-hydrogen for air traffic control
A 19.8 kW PV system is powering a telecommunications antenna at a French air control centre. When it produces more energy than needed, the surplus is used to produce hydrogen which is then utilised to produce new electricity via a fuel cell system and provide power to the antenna during a period of up to five days. For short-term storage, lithium-ion batteries are used.