Coalition’s $1.4b ARENA extension cuts solar and wind while enabling fossil fuels
The Australian Government has finally announced new long term funding and an expanded remit for the Australian Renewable Energy Agency (ARENA) beyond 2022. The funding package, which looks more like a cut than anything else, pushes investment away from solar and wind and toward fossil fuel enabling technologies like carbon capture and storage.
UNSW doctoral student’s solar fairytale wins 3 Minute Thesis Final
UNSW Faculty of Engineering doctoral researcher Bruno Vicari Stefani won the University’s Virtual 3 Minute Thesis Final by creatively reimagining the fable of the Three Little Pigs to demonstrate how combining hydrogen with low-cost silicon in solar can improve efficiency.
SNEC 2020 CEO Series – Interview with Liu Zhifeng, Vice GM of Jolywood
Jolywood is one of the few PV manufacturers, who has placed its bet on TOPCon technology. Instead of focusing on the simplicity of the production process, Jolywood believes the conversion rate is more critical. With years of efforts, the company has established its leading position among TOPCon players. During the SNEC 2020 in Shanghai, pv magazine had the opportunity to interview Liu Zhifeng, Vice General Manager of Jolywood, and listened to his views on some hot topics, especially the cell tech route.
Photovoltaic shade for greenhouses
French start-up Solar Cloth has secured a patent for a PV shade screen for solar greenhouses.
Heating up the heterojunction-LID discussion
Scientists led by the University of New South Wales have looked into the long-term degradation of silicon-heterojunction. Their findings suggest that illumination at high temperatures could actually improve cell efficiency, but also risks activating multiple light-induced degradation mechanisms if not carefully controlled.
Floating PV to offset underperforming hydropower
Brazil now has 12 GW of underperforming hydropower capacity, according to U.S. researchers. Large-scale floating PV is an ideal solution to offset this shortfall, due to its high capacity factor, load correlation, and high potential output during periods of high demand.
Windbreak walls for solar farms
Iasol has developed a new way to protect solar plants in windy conditions. The Spanish developer said the solution barely has an impact on project costs or output, while preventing expensive damages.
Green light for the $300 million green Bundaberg Hydrogen Hub
The first of three large-scale green hydrogen plants in the pipeline of the Green Hydrogen Australia Group has been given the green light. The Bundaberg Hydrogen Hub, featuring an 80 MW hydrogen electrolyser, will produce clean hydrogen for Australian hydrogen vehicle developer H2X.
Solar-plus-storage for the Cook Islands
Around 4.2 MWh of energy storage capacity will be connected to a solar and diesel micro-grid on Rarotonga, the largest of the islands in the South Pacific nation. Three 40-foot containers with a total power output of 4.8 MVA will be used as a power reserve and for grid support by utility Te Aponga Uira.
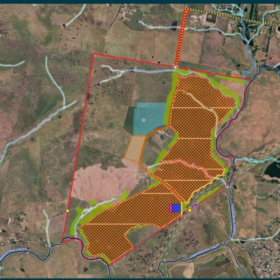
Australia’s first large scale solar garden – city dwellers of the world, unite!
Almost a third of Australians are locked behind the solar barrier, they’re renters, tenants, urban apartment-dwellers who don’t have the luxury of installing their own solar PV. However, now city-dwellers can participate in the solar transition too, by becoming members of the Haystacks Solar Garden which operates in much the same way as community garden.