Novel tool for PV system sizing allows users to assess tradeoffs between reliability and costs
Developed by scientists in Egypt, trhe Green Energy Solutions software allows users to assess the tradeoffs between the PV system reliability and its costs. Compared to PVsyst, it has an error margin of up to 9%.
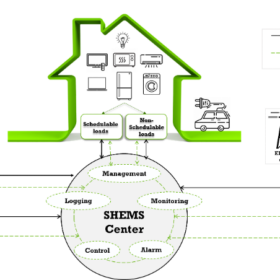
Energy management system to combine residential PV with gravity storage
Researchers in Morocco have created a new energy management system that allows the combination of rooftop PV with gravity storage. The proposed system is reportedly able to perform smart energy distribution within a household while also lowering electricity costs.
The Hydrogen Stream: China starts world’s biggest solar-to-hydrogen site
China’s Sinopec has switched on the world’s largest solar-to-hydrogen project in Xinjiang, while India has unveiled a new plan to incentivize green hydrogen and electrolyzer production.
Electrolysis cost-efficient in all climates, says Finnish team
Researchers at the VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland said that chemical energy storages were needed for short and long-term balancing in every climate region, especially in the northern climates. Meanwhile, companies are moving forward with their plans to produce hydrogen in Namibia and Morocco.
World’s largest hydrogen airplane makes first flight
The hydrogen stream: ZeroAvia tested its new 19-seat hydrogen-powered aircraft, Chinese scientists unveiled new tech to promote bubble removal in electrolysers, and Egypt-Japan University of Science and Technology researchers claimed that the most efficient hydrogen production systems are based on waste heat.
Hydrophobic nanocoating to reduce soiling in solar panels
Scientists in Egypt have created a self-cleaning, hydrophobic coating for solar panels that reportedly increases their efficiency by more than 30%. They used a coating solution based on polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and silicon dioxide (SiO2) nanocomposites, mixed with ethanol and isopropanol.
Germany to import green ammonia from Saudi Arabia from 2026
Germany has decided to build its first green ammonia import terminal in Hamburg, in collaboration with Air Products. Egypt, meanwhile, has signed $128 billion of hydrogen framework agreements.
Off-grid solar continues to expand
The off-grid solar sector has shown resilience in the face of pandemic-related challenges, with 70 million people gaining access to electricity from early 2020 to the end of 2021. However, the ability to pay for solar energy kits has taken a hit.
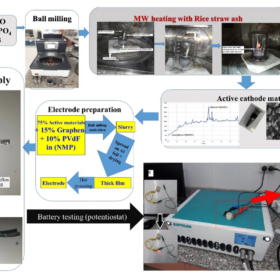
Ultra-fast synthesis of nanocomposites for sodium ion batteries, supercapacitors
Researchers in Egypt have developed a synthesis method that uses the high microwave absorbance of silicon carbide content in rice straw ash and takes just 60 seconds to produce sodium iron phosphates-carbon nanocomposites (NaFePO4-C), which can be used as sodium ion battery cathodes and as symmetric supercapacitors.
Fortescue proposes 9.2 GW green hydrogen project in Egypt
Mining magnate Andrew Forrest’s Fortescue Future Industries continues its campaign to be one of the world’s largest clean energy companies, announcing plans to develop a 9.2 GW wind and solar facility in Egypt that will power green hydrogen production in the Arab republic.