Sun Cable customer exits as energy price rises take toll
The world’s biggest solar PV and storage project has suffered a setback after a Singapore electricity retailer which had lined up to be a foundation customer for the renewable energy generated by Australia’s $26 billion Sun Cable project announced it will cease operations amid a record-breaking spike in electricity prices.
Fortescue links with Plug Power to build electolyser gigafactory
Fortescue Future Industries has revealed it will partner with North American hydrogen technology company Plug Power to build the world’s largest green energy infrastructure and equipment-manufacturing facility in Central Queensland.
Morrison confirms he will attend COP26 climate summit
Australian Prime Minister Scott Morrison has confirmed he will travel to Scotland for the United Nations COP26 international climate conference later this month, signalling an about-turn after he had previously indicated he might not attend the talks.
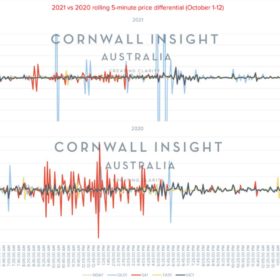
I’m pickin’ up good vibrations: 5-minute settlement reviewed
We are just through the first two weeks of 5-minute settlement. While there has been much anticipation regarding the implementation and the potential for drastic swings in prices, we felt it was an excellent time to take a quick look at the pricing outcomes to see if any immediate trends are emerging.
Coles secures path to 100% renewable energy by 2025
Supermarket giant Coles will be 100% powered by renewable energy in less than four years’ time after the company announced the last of the power purchase agreements needed to meet the ambitious target were signed this week.
The net-zero bandwagon is gathering steam, and resistant MPs are about to be run over
Prime Minister Scott Morrison appears to be moving towards securing Coalition agreement for a net-zero emissions by 2050. It comes weeks out from the crucial COP26 climate talks in Glasgow, where Australia’s record on global climate action will be heavily scrutinised.
States pave way for Morrison to beat 2030 emissions pledge
With Prime Minister Scott Morrison under increasing pressure to back a 2050 net-zero carbon emissions target before the United Nations’ COP26 climate conference in Glasgow at the end of the month, a new report indicates the federal government can capitalise on state and territory efforts to keep the global 1.5°C goal in play.
BHP inks supply deal with Australia’s largest wind+solar farm
Mining giant BHP is poised to finalise a “bespoke” renewable energy agreement with the Australian arm of Spanish energy group Iberdrola for the 317 MW Port August Renewable Energy Park in South Australia to supply up to 50% of the miner’s electricity needs for its Olympic Dam mining operation.
Solar installer fined $500,000 after string of safety breaches
A Victorian solar installer has been fined $500,000 for a string of workplace safety breaches, including a 2019 incident where a worker suffered serious injuries after falling through a skylight.
Australia’s largest solar supplier expects shortfalls and up to 30% prices hikes as global stock contest escalates
Australia’s largest wholesale solar distributor is expecting shortfalls of supply coupled with 20% to 30% cost increases as a result of the energy crisis in China. The situation in Australia is particularly fragile, pv magazine Australia was told, with our low pricing and the comparable size of our market not playing to our favour in the global battle for solar supplies.