Fortescue Metals Group (FMG), whose executives and chairman, Andrew “Twiggy” Forrest, have been putting the company jet through its paces over the last year, signing green energy deals from Papua New Guinea to Jordan, has contracted Pacific Energy subsidiary Contract Power Australia (CPA) to build Western Australia’s (WA) largest network integrated battery energy storage system (BESS).
The 42 MW battery project will see CPA design, construct, test, install and commission two batteries for FMG subsidiary Pilbara Energy as part of FMG’s integrated power network in the Pilbara region.
Much of the workload will be forked off to Pacific Energy subsidiary Hybrid Systems Australia, whose executive director, Michael Hall, said the long-standing remote generation experience of Contract Power combined with Hybrid Systems’ industry leading BESS deployment and network integration expertise demonstrated the industry capabilities that exist within Western Australia and Australia to deliver world class projects.”
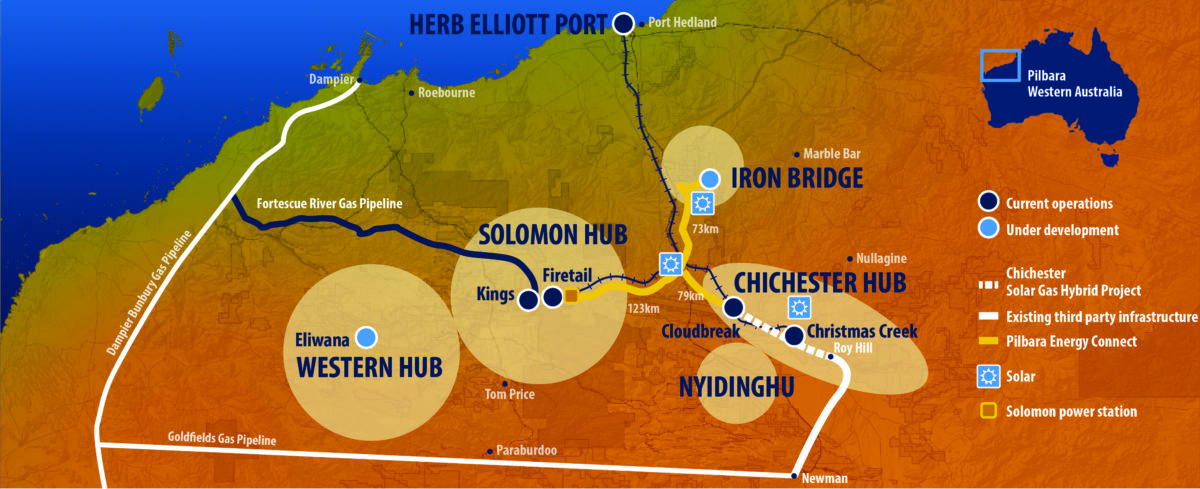
The move is part of FMG’s emissions reduction goal to achieve carbon neutrality by 2030. To do this, FMG’s Energy Strategy includes strong investment in renewables and low emissions energy sources, including almost $700 million in the next stage of its Pilbara Energy Connect program to combine 150 MW of gas-fired generation with 150 MW of solar PV and the aforementioned grid-scale battery.
The hybrid generation project will provide low cost power to the Iron Bridge magnetite project currently under construction. The battery was previously planned to be 35 MW/11 MWh, but that seems to have risen to 42 MW.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.








3 comments
By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.