Indonesian think tank says nation at crossroads with energy transition
Indonesian clean energy policy think tank, the Institute for Essential Services Reform (IESR), said 2025 will be a pivotal year for Indonesia’s energy transition, as the nation has fallen behind targets in recent years.
EliTe Solar opens solar cell production facility in Indonesia
Just a few months after beginning construction on a cell manufacturing factory in Egypt, Singapore’s EliTe Solar has opened a cell manufacturing facility in Indonesia, which took around eight months to complete from site selection to opening.
Thornova Solar starts cell, module production in Indonesia
United States manufacturer Thornova Solar has started producing solar cells and modules in Indonesia. CEO William Sheng says the move is in line with changing US market regulations. It plans to supply customers with cells and modules from Indonesia, Laos or the US by mid-2025.
Indonesia teams with CATL to deliver 15 GWh capacity battery cell plant
Indonesia has struck a deal with Chinese battery industry heavyweight CATL to build a giga-scale battery cell manufacturing plant in the southeast Asian nation as it works to establish a battery and electric vehicle ecosystem.
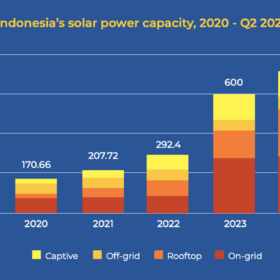
Indonesia’s installed solar capacity surpasses 700 MW
The Institute for Essential Services Reform says Indonesia’s solar industry has faced a downturn over the past two years, but policy reforms should accelerate solar deployment in the coming years. The think tank’s latest report states that 16.92 GW of projects are currently in the pipeline across the country.
Gstar introduces 440 W TOPCon solar module with framless design
The Singapore-based manufacturer said its new panel can achieve self-cleaning through rainwater thanks to its frameless design. The new product features an operating temperature coefficient of -0.30% per C and an efficiency ranging from 21.51% to 22.53%.
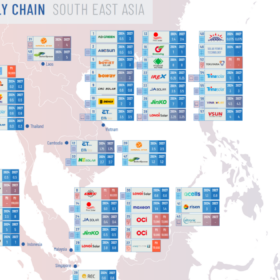
Sinovoltaics tracks 78.8 GW solar module capacity in Southeast Asia
The latest supply chain map from Sinovoltaics tracks growth across Southeast Asia, with module capacity reaching 78.8 GW, and 58 production projects tracked.
USA module manufacturer SEG Solar turns sod on 5 GW Indonesian plant
United States-headquartered solar module manufacturer SEG Solar has started building 10 N-type cell production lines in Indonesia’s Kawasan Industri Terpadu Batang industrial park, 390 kilometres east of Jakarta.
Singapore progresses its 4 GW clean energy import ambition with new agreements
Singapore has progressed its ambition to import 4 GW of low-carbon electricity by 2035 from neighbouring countries, which includes from Australia’s SunCable project, with the signing of two new agreements.
A 100% solar Indonesia in 2050
Indonesia has all the solar energy and pumped-hydro energy storage potential required to become a solar giant by mid-century. On current trends, Indonesia will be the fourth largest producer of solar energy by 2050.