PV modules with longer lifetimes could slash demand for materials, says NREL
The US National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) says in a new report that PV module lifetime extensions should be prioritised over closed-loop recycling to reduce demand for new materials.
Globalised supply chains saved $103 billion in solar panel production costs
A new study has calculated that the globalised PV module supply chain has saved billions for PV installers in Germany, the US and China. It also found that if strong nationalistic policies that limit the free flow of talent and capital were implemented going forward, solar panel costs would be 20-25% higher by 2030.
Cooling down solar modules by increasing space between panel rows
A US research team claims to have demonstrated that increasing the spacing of solar panels between rows improves PV system efficiency and economics by allowing airflow to cool down the modules. The method could improve a project’s LCOE by as much as 2.15% in certain climates.
Non-flammable, graphene-based lithium-ion batteries approaching stationary storage market
US-based Nanotech Energy’s graphene battery uses proprietary electrodes with a thermally stable separator, and non-flammable electrolyte that is said to be inexpensive to manufacture. The technology is said to be superior in terms of safety and competitive in terms of cell performance.
Rooftop wind energy innovation claims 50% more energy than solar at same cost
BASF is currently testing Aeromine Technologies’ patented motionless wind-harvesting system.
Global polysilicon capacity could hit 536 GW by end of 2023
Clean Energy Associates said in a new report that it expects polysilicon production capacity to exceed PV installations next year.
Wind, solar payback times under a year in some parts of world, says Rystad
Record energy prices, particularly in Europe, are driving demand for renewables and energy storage. That is changing the equation for utility solar and wind investment and shortening project payback times to under a year in some regions. Storage deployment, driven by recent policy developments around the world, is also expected to get a big boost through to 2030.
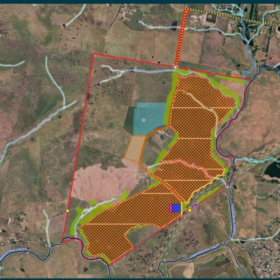
Quinbrook sells share in giant US solar and storage project
Australia-based energy investment manager Quinbrook Infrastructure Partners has sold a 49% stake in a massive $1.9 million (USD 1.2 billion) solar PV and battery energy storage project being developed in the United States to a Dutch pension asset manager.
Vast Solar lands US support for CSP technologies
Australian company Vast Solar’s plans to expand into the rapidly growing North American renewable energy market have received a multi-million dollar boost after the United States government announced more than $38 million (USD 24 million) in grants to advance the development of concentrated solar thermal power technologies.
Pairing batteries with rooftop solar
A growing number of residential solar projects include energy storage batteries. In the first part of this series, we look at the backup power feature of batteries.