Potentia Energy, a joint venture between Italy-headquartered Enel Green Power and Japan’s Inpex Corporation, confirmed that the Australian government has officially approved its Tallawang Solar Hybrid project under the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation (EPBC) Act.
In a notice on the EPBC portal, the Tallawang solar hybrid project was marked as “approved without conditions,” paving the way for the project to go ahead.
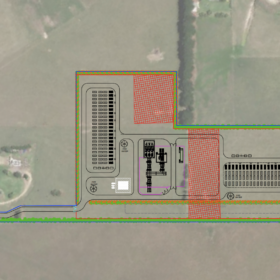
The Tallawang project proposes to combine a 500 MW solar farm with a DC-coupled 500 MW / 1,000 MWh battery energy storage system (BESS), enabling it to store the solar energy on site and send it to the grid in the evening peaks.
The facility is to be built across a 1,300-hectare site about eight kilometres northwest of Gulgong, in the heart of the New South Wales (NSW) government’s Central-West Orana Renewable Energy Zone (REZ) and once operational, will generate clean energy to power the equivalent of more than 250,000 homes each year.
Potentia Energy Chief Executive Officer Werther Esposito said being granted environmental approval was a critical step, adding the company would continue to proactively work with and engage the local community.
“We look forward to continuing to work closely with the local community, our host landowners and project partners to deliver Tallawang in a way that genuinely maximises long-term benefits for the region,” he said.
Potentia is targeting start of construction in early 2027, indicating the delivery timeframe will be aligned with the delivery of the Central-West Orana REZ transmission project. The project is expected to support up to 420 jobs during the estimated three-year construction phase.
The EPBC decision comes just weeks after the NSW Independent Planning Commission (IPC) granted its approval for the solar and battery hybrid project.
The Tallawang project, originally developed by British-based global energy company Renewable Energy Systems, is part of Potentia’s growing portfolio of assets across Australia.
Formerly known as Enel Green, Potentia is aiming to build more than 7 GW of renewable energy projects in the country, targeting investments in wind, solar, storage, and hybrid technologies.
Some of the company’s key projects include the operational 93 MW Girgarre and the 27 MW Cohuna solar farms in Victoria in Victoria, and the Bungala One and Two solar projects in South Australia, which together have a capacity of 220 MW.
It is also progressing plans to build a 225 MW / 900 MWh battery energy storage system alongside the Bungala solar facility, and is also building the Quorn Park hybrid project, that will combine a 96 MW solar farm and 20 MW / 40 MWh battery energy storage system, in the central west of NSW.
This content is protected by copyright and may not be reused. If you want to cooperate with us and would like to reuse some of our content, please contact: editors@pv-magazine.com.








1 comment
By submitting this form you agree to pv magazine using your data for the purposes of publishing your comment.
Your personal data will only be disclosed or otherwise transmitted to third parties for the purposes of spam filtering or if this is necessary for technical maintenance of the website. Any other transfer to third parties will not take place unless this is justified on the basis of applicable data protection regulations or if pv magazine is legally obliged to do so.
You may revoke this consent at any time with effect for the future, in which case your personal data will be deleted immediately. Otherwise, your data will be deleted if pv magazine has processed your request or the purpose of data storage is fulfilled.
Further information on data privacy can be found in our Data Protection Policy.