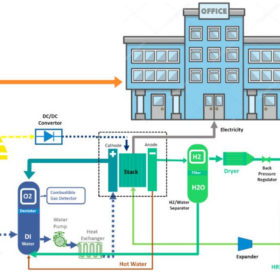
Cost comparison between lithium batteries, fuel cells, reversible solid oxide cells as storage for off-grid rooftop PV
Scientists in the United Arab Emirates have looked at how off-grid rooftop PV could be combined with batteries, fuel cells or reversible solid oxide cells for energy storage. The modelling assumed a typical commercial building in Los Angeles.
Amazon invests in novel solar cell production facility
Ambient Photonics will build a fully automated manufacturing facility to produce solar cells for powering consumer electronics.
New Zealand unveils multibillion-dollar climate plan, comes under attack for ‘staggering’ omission
New Zealand’s government this week unveiled its plan to cut emissions and fund the clean energy transition, featuring policies like a ‘scrap and replace’ scheme to incentivise electric vehicles and funding for electrifying industry. The NZ$2.9 billion (AU$2.6 billion) plan has received mixed reviews, with Greenpeace saying it has overlooked the country’s most glaring problem.
Emissions-free battery recycling facility will use electricity rather than smelting
ACE Green Recycling has announced plans to build a new plant in Texas to recycle both lead-acid and lithium-ion batteries.
UNSW researchers crack ‘night-time’ solar
Researchers from the University of New South Wales have made a major breakthrough in what was previously conceived of only in theoretical terms, namely, ‘night-time’ solar power.
Regulator’s hydrogen certification scheme secures 17 projects
The Commonwealth government backed Clean Energy Regulator on Tuesday confirmed 17 hydrogen projects across Australia have signed up to participate in its ‘Guarantee of Origin’ scheme.
Water ‘secret ingredient’ in new processing mechanism for perovskite nanocrystals
An unlikely union has been discovered by members of ARC Centre of Excellence in Exciton Science, who have found a way to control the growth of phase-pure perovskite crystals for next-generation photovoltaics using water.
Smarter E products at a glance
pv magazine summarises the products we covered at the recent Smarter E exhibition, in the first of a series of reports on all of the new releases from the annual trade fair in Munich, Germany.
Hydrogen fuel cell without precious metals developed, Australia’s global importance underscored in Rotterdam
A team of researchers from the University of Wisconsin-Madison, Cornell University, and Wuhan University have presented a completely precious metal–free alkaline fuel cell with enhanced performance using a carbon-coated nickel anode. Meanwhile, the Port of Rotterdam has offered to supply northwestern Europe with 4.6 million tonnes of hydrogen by 2030. According to RMI, Europe will import green hydrogen between 2024 and 2030. RenewableUK sees room for hydrogen exports from the UK to the EU.
Heat-storage building material to passively cool PV systems, batteries
German researchers have developed a new shape-stabilised phase change material with the ability to store up to five times more thermal energy than commercially available phase change materials (PCMs).