China’s first salt cavern for compressed air energy storage goes online
Huaneng Group has finished building a 300 MWh storage project in Changzhou, in China’s Jiangsu province. The state-owned company has already started operating the facility, which is situated in a salt cavern.
Trina Solar’s pathway to TOPCon
Trina Solar will eventually start selling TOPCon and heterojunction products, even though it built its first large-scale TOPCon project four years ago. The company says it is now making progress on TOPCon module production, despite supply chain issues.
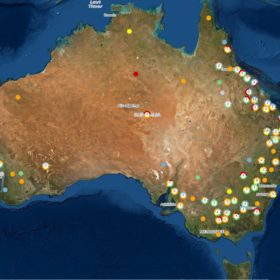
Australian solar projects catalogued by global mapping tool
United States-based data company Global Energy Monitor has launched a new open-source tool that lists Australia’s large-scale solar plants alongside those from another 147 countries.
Novel tech for extracting hydrogen gas from liquid carriers
North Carolina State University (NCSU) has developed an energy-efficient strategy for room-temperature hydrogen release from liquid hydrogen carriers, which uses less rhodium. Elsewhere in the world, Airbus launched its Zero Emission Development Centre in the UK, Toshiba ESS teamed up with Fusion Fuel to target Australian and European markets, and Corfo signed agreements to finance three renewable hydrogen projects with GNL Quintero, iCAP, and Air Liquide in Chile.
JA Solar introduces n-type solar panel with 22.4% efficiency
JA Solar said the smallest solar panel in its new n-type product line has a power output of 435 W and a power conversion efficiency of 22.3%. The largest module in the series has an efficiency rating of 22.4% and 625 W of nominal power. Their temperature coefficient is -0.30% per degree Celsius.
VSUN strikes deal to explore redox flow battery technology
Western Australian energy storage company VSUN Energy has inked a deal with aspiring renewables developer North Harbour Clean Energy which will see the two companies collaborate on the development and installation of vanadium redox flow battery projects and vanadium electrolyte supply.
China dominates transport fuel-cell patents
The World Intellectual Property Organisation says China accounted for 69% of the patents filed for transport-related fuel-cell tech in 2020, with road transport significantly dominating applications.
Mine shaft gravity storage startup completes capital raise as it preps for demonstration
Green Gravity, a startup proposing to use old mine shafts for gravitational energy storage, has raised $1.4 million in its first formal capital raise. The company, headed up by former BHP executive Mark Swinnerton, is now finalising its concept engineering in preparation for its demonstration plant. “I think we’re going to get the ‘and’ here,” Swinnerton told pv magazine Australia, referring to the technology’s potential to provide low cost firming (and more) by using yesterday’s infrastructure to solve today’s problem.
Upcycling silicon waste from end-of-life solar panels into thermoelectrics
Researchers in Singapore have developed a new technique in which polycrystalline silicon is pulverised into powder and pelletised into ingots. The process relies on spark plasma sintering to dope the silicon with germanium and phosphorus.
Gallium doping and solar cell degradation
German scientists have conducted a series of experiments on gallium-doped silicon solar cells to understand the causes of degradation in PV cells and modules treated with gallium rather than boron. They confirmed that the performance losses are caused by a bulk defect in the material, and found that the right combination of light and temperature can “heal” earlier damage and even lead to small improvements in overall cell efficiency.