IEA lowers 2025-30 forecast for solar growth
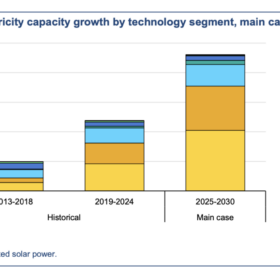
The International Energy Agency has cut its 2025–30 renewables forecast by 5%, citing lower solar additions, though PV still represents nearly 80% of 4.6 TW expected growth.
Operational faults cut returns in 19% of battery storage projects
A recent report from battery intelligence firm Accure reveals that while most battery energy storage systems operate reliably, nearly 19% of projects experience reduced returns due to technical issues and unplanned downtime.
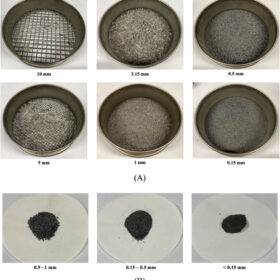
New sieving tech for solar cell silver recovery
Researchers at University of New South Wales have reported details about a novel sieving-aids technology that improves the separation of metal fragments from other components when recycling end-of-life PV panels. The patented process reportedly enhances the recovery of silver.
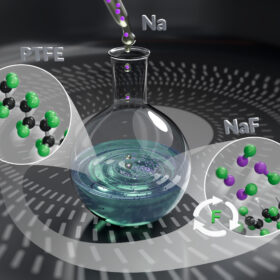
Novel fluorine recovery method promises polymer recycling benefits
Researchers have developed a novel defluorination method to dispose of PTFE, used in solar componentry and electric cable coating, that converts its constituent fluorine compounds and could enable eco-friendly polymer recycling.
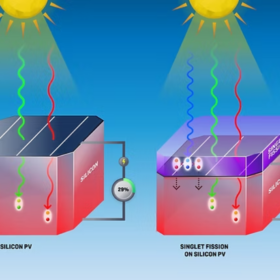
Singlet fission research breakthrough unlocks high solar cell efficiency
University of New South Wales researchers have filed patent protection and are working to scale production of a new class of photostable organic molecules proven to boost silicon solar cell efficiency, reduce heat and extend panel lifetimes using singlet fission.
KAUST achieves 28.7% efficiency in perovskite-perovskite-silicon tandem solar cell
An international team of researchers led by King Abdullah University of Science and Technology has fabricated a triple junction perovskite-perovskite-silicon tandem solar cell that achieved a world record efficiency for this cell architecture. The device incorporates stabilised perovskites that ensure improved performance and stability.
New algorithms boost dual-axis solar tracker performance
Researchers in Australia and India have developed two solar tracker optimisation techniques that can purportedly increase power generation by up to 54.36% when combined. One uses a light sensor and the other relies on data from GPS and a real-time clock.
Monash engineers boost zinc-air battery performance with cobalt-iron catalyst
Engineers at Monash University in Melbourne have developed a new catalyst they say could bring zinc-air batteries “closer to real-world, grid-scale and transport uses.”
Renewables reach record 77.9% share in NEM
The share of renewables in Australia’s main electricity grid continues to reach new highs, delivering 77.9% of electricity demand on Sunday with solar power contributing more than 55% of the record-breaking clean energy mix.
Solar cell study boosts efficiency beyond 20% using caesium bromide interlayer
A new collaborative study between six universities, including three in Australia have published breakthrough findings demonstrating how caesium bromide, can dramatically improve the efficiency of crystalline silicon solar cells.