Novel tech to recycle silver, aluminum from end-of-life solar panels
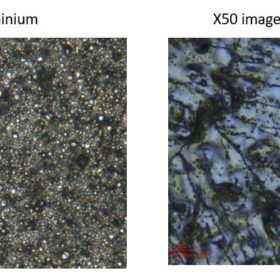
Researchers in the United Kingdom have developed a new method of extracting silver and aluminium from end-of-life PV cells using iron chloride and aluminium chloride dissolved in brines. According to the research team, the cheap solvents retrieve up to 95% of the metals within 10 minutes, achieving a 98% purity of silver chloride.
UK investment firm makes $36 million move into NSW solar market
United Kingdom-headquartered investment firm Global Sustainable Energy Opportunities has increased its Australian solar PV portfolio, committing $36 million (£21.2 million) to acquire three more solar projects with a combined capacity of 15 MW.
UK startup unveils solar trees for commercial, industrial areas
United Kingdom-based SolarBotanic Trees will begin offering its solar trees in early 2023. The systems will use monocrystalline cells with an efficiency of up to 24%, encapsulated in a 3D shape.
Dye-sensitised photocatalyst promises most efficient solar water splitting to date
Japanese researchers have developed a new way to improve water splitting, while South Korea has completed its largest hydrogen production complex. Scotland and England have announced new hydrogen investments, and Uzbekistan and Saudi Arabia’s ACWA Power have agreed to collaborate on hydrogen projects.
Optical microscopy technique to study prevention of battery failure
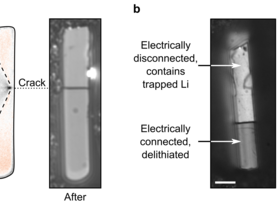
Researchers at the University of Cambridge have examined one of the fastest-charging anode materials by using a low-cost, lab-based optical microscopy technique. Their findings showed that particle fracture, which can reduce the storage capacity of a battery, is more common with higher rates of delithiation and in longer particles.
Traditional hydrogen blending could damage gas pipelines, say researchers
UK researchers have revealed that gaseous hydrogen could cause problems in natural gas pipelines, while electrolyser manufacturer Nel has announced plans to build a second production line in Norway.
Small cracks have negligible effect on solar cell performance
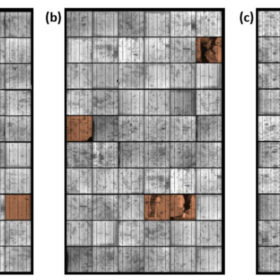
A team of researchers from the United Kingdom have found that crack percentages of up to 11% have a very limited impact on solar cell performance. They also ascertained that hotspots are likely to arise when the crack percentage is in the range of 11 to 34%.
The real value of energy storage
An international research team has developed a new way to evaluate the economic value of energy storage technologies. They went beyond pure cost assumptions to consider the benefits that such technologies could bring to energy systems.
Lithium-ion vs. vanadium redox flow storage
UK scientists have compared the performance of lithium-ion storage systems and vanadium redox flow batteries for a modeled 636 kW commercial PV system in southern California. They have found that both technologies, coupled with an oversized PV array, could achieve a levelised cost of electricity of less than US$0.22/kWh (AU$0.32/kWh), while offering a self-sufficiency ratio of 0.95.
UK government warns of global warming risks related to hydrogen leaks
The UK Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy has published new research showing that hydrogen leaks could have an indirect climate-warming impact, partly offsetting efforts to reduce carbon dioxide emissions.