Squadron begins work on $3 billion Queensland wind and solar hub
Australian resources company Squadron Energy has commenced construction on a 1.2 GW hybrid wind, solar and battery energy storage project in Central Queensland that is expected to deliver crucial capacity into the grid as Australia transitions to a renewable energy future.
‘Missing piece of the puzzle’: 3 GW of battery projects make it to ARENA’s grid forming shortlist
ARENA today announced 12 projects with a combined capacity of 3 GW are on the shortlist for its $100 million Large Scale Battery Storage Round which aims to support to rollout of storage fitted with grid forming capacities.
Stanwell plans 2.9 GWh big battery next to coal unit
Queensland government-owned energy generator Stanwell has revealed plans to a build a massive 1.45 GW/2.9 GWh battery storage system alongside the coal-fired Stanwell Power Station in central Queensland as the state government looks to ramp up energy storage capacity to support the transition to renewables.
Liontown gives $545 million lithium project go-ahead after locking in Ford offtake deal
Australian miner Liontown Resources has declared the way is now clear for construction to commence on its $545 million Kathleen Valley Lithium Project in Western Australia after inking an offtake agreement and $300 million financing facility with global car manufacturing giant Ford Motor Company.
Coal plant closures adds sense of urgency to energy transition
The quickening exit of coal-fired generation from Australia’s energy mix – with 60% of capacity expected to be withdrawn from the National Electricity Market by 2030 – has emphasised the need for significant investment in renewable energy generation, storage, transmission, and system services.
AEMO reveals new roadmap for rapid switch to renewables
The Australian Energy Market Operator has declared approximately $12.7 billion of investment in new transmission lines should begin “as urgently as possible” to accelerate the transition to renewable energy and energy storage, replace exiting coal-fired power plants, and deliver a more efficient and effective grid in eastern and south-eastern Australia.
Tesla big battery operator fined for power rules breach
The operator of the 150 MW/193 MWh Hornsdale Power Reserve in South Australia has been fined $900,000 after being sued by the Australian Energy Regulator for failing to deliver on its promise of providing services essential to maintaining the stability of the power grid.
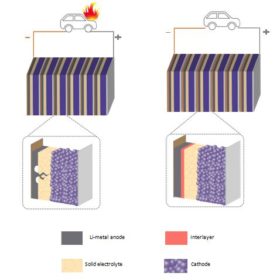
Indian researchers find way to stop dendrites in solid-state lithium batteries
Researchers from the Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore, have found that nanoscopic refractory metal layers like tungsten could improve dendrite growth tolerance in electrolytes of solid-state Li-ion batteries. The team collaborated with researchers from Carnegie Mellon University.
CS Energy unveils plans for Queensland’s biggest battery
Queensland government-owned generator CS Energy has announced plans to build the largest grid-scale battery in the state at Greenbank in Brisbane’s outer southern suburbs. The 200 MW/400 MWh project will be delivered in partnership with Queensland network operator Powerlink.
Longi unwraps reasons behind green hydrogen shift
In recent years, Longi has turned its attention to green hydrogen. Li Zhenguo, company founder and CEO, speaks with Vincent Shaw in Shanghai about the strategic shift and how coupling this technology with solar PV will be key to achieving carbon neutrality.