Melbourne-based 8 Star Energy set to shine in Europe
Melbourne-based 8 Star Energy has been announced as a distribution partner alongside Germany-based Memodo as world leading battery brand Energizer launches its Energizer Solar PV portfolio across Europe.
Shark Lake Renewables Hub cuts Esperance emissions by 50%
Western Australian Premier Mark McGowan and Energy Minister Bill Johnston were in attendance yesterday when Horizon Power and Pacific Energy officially opened the Shark Lake Renewables Hub, which features 4 MW of solar alongside wind turbines, battery energy storage and a gas power plant.
Test production starts at SolarEdge’s 2 GWh Korean battery cell fab
The inverter and battery manufacturer says its new Sella 2 factory will produce cells for its residential solar-plus-battery products as well as for other applications.
VSUN strikes deal to explore redox flow battery technology
Western Australian energy storage company VSUN Energy has inked a deal with aspiring renewables developer North Harbour Clean Energy which will see the two companies collaborate on the development and installation of vanadium redox flow battery projects and vanadium electrolyte supply.
ACEN commences construction of New England big battery
The Australian arm of Philippines-based clean energy company AC Energy has commenced construction of a 50MW/50MWh battery energy storage system that will be connected to its 720MW New England Solar Farm being developed near Uralla in northern New South Wales.
Mine shaft gravity storage startup completes capital raise as it preps for demonstration
Green Gravity, a startup proposing to use old mine shafts for gravitational energy storage, has raised $1.4 million in its first formal capital raise. The company, headed up by former BHP executive Mark Swinnerton, is now finalising its concept engineering in preparation for its demonstration plant. “I think we’re going to get the ‘and’ here,” Swinnerton told pv magazine Australia, referring to the technology’s potential to provide low cost firming (and more) by using yesterday’s infrastructure to solve today’s problem.
Sungrow’s new battery to be deployed in 16 mid-scale Victorian solar farms from Lavo
Chinese inverter brand Sungrow has signed a 79 MW inverter and 176 MWh battery energy storage contract with Sydney-based hydrogen battery company Lavo. The contract will see Sungrow add its storage solution to 16 mid-scale solar farms in Victoria.
Virtual power plant technology on trial in NSW schools
The New South Wales government has announced plans to use part of an estimated eight million square metres of public school roof space to install rooftop solar PV as it seeks to test the most effective ways to generate, store and export renewable energy into the state’s electricity grid.
Consumer watchdog sounds warning for LG-branded home batteries
The Australian Competition and Consumer Commission has issued a call for homeowners to urgently check their residential energy storage systems amid a national recall of some LG-branded batteries which may overheat and ignite.
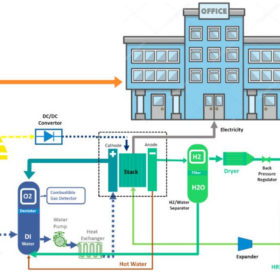
Cost comparison between lithium batteries, fuel cells, reversible solid oxide cells as storage for off-grid rooftop PV
Scientists in the United Arab Emirates have looked at how off-grid rooftop PV could be combined with batteries, fuel cells or reversible solid oxide cells for energy storage. The modelling assumed a typical commercial building in Los Angeles.