Influx of new companies and products enter Australia’s battery market
Battery companies hoping to get a foothold in Australia’s rapidly growing storage market were the main exhibitors at the Smart Energy Conference held in Sydney last week, outnumbering solar companies almost two-to-one. Pv magazine Australia looked at what is on offer and who the new hopefuls in the battery space are.
New entrants to Australia’s utility-scale and commercial battery market
While Australia’s home battery market seems to have attracted most of the interest from newcomers, there has been some significant new developments in the commercial and utility-scale space. Pv magazine Australia examined the new products and companies in the commercial and utility battery storage space on display at the Smart Energy Conference.
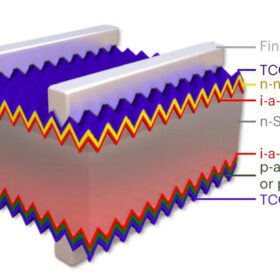
A closer look at Longi’s world record-breaking, 26.81%-efficient heterojunction solar cell
An international research group led by Longi Central R&D Institute has published a paper describing Longi’s heterojunction solar cell based on a full-size silicon wafer that made a sensation in November, as it beat the long-lasting efficiency record held by Japanese manufacturer Kaneka for years. The researchers attributed the cell efficiency improvement to the implementation of a p-type amorphous silicon hydrogenated layer together with a modified transparent conductive oxides contact, which they said greatly reduced the cell contact resistivity.
Strong revenue growth for biggest Chinese solar panel makers in Q1
JinkoSolar, Long, JA Solar, and Trina Solar have all reported impressive growth figures for the first quarter of this year.
Weekend read: Solar’s supply-chain pioneer
Zhengrong Shi and his company, Suntech, are true pioneers of the Chinese solar industry. While Suntech burned bright, and eventually flamed out, under Shi’s leadership, the company’s solar ecosystem and innovation persist as China’s PV market surges past 100 GW(AC) today.
Risen rolls out new n-type panels in Australian market
Chinese solar module maker Risen Energy has launched two new n-type panels into the Australian market, targeting both the rooftop and large-scale PV markets.
Construction begins on solar cycling path in Netherlands
Local government in the Dutch province of North Brabant will deploy a 500-metre-long solar array on a bike track and test its performance over a five-year period. The PV system will be integrated into the asphalt top layer and will consist of 600 solar panels of an unspecified type.
Solar assets are underperforming expectations by 8%, what is the root cause?
The Renewable Energy Test Center (RETC) raised the issue of ultraviolet-induced degradation of the trending technology in its PV Module Index 2022.
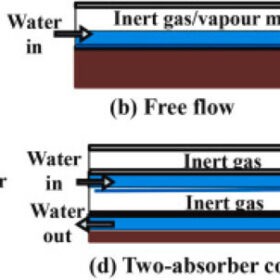
All photovoltaic-thermal system designs at a glance
An international research team has presented all possible system designs and applications for photovoltaic-thermal (PVT) technology. Their review includes conventional PV-T collectors, air-based systems, liquid-based installations, water-based collectors, refrigerant-based systems, heat-pipe-based technologies, dual air-water systems, building-integrated PVT arrays, and concentrated PVT collectors.
Swiss manufacturer enters Australia with heterojunction solar module
Swiss solar module maker Meyer Burger plans to grab a share of the booming Australian PV market, announcing it will start selling a series of high-performance solar panels that the company says deliver higher energy yields when compared to conventional technologies.